|
2006 World Baseball Classic
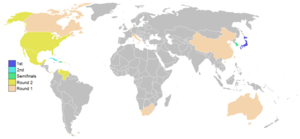 The 2006 World Baseball Classic (WBC) was the inaugural tournament between national baseball teams that included players from Major League Baseball. It was held from March 3 to 20 in stadiums in or around Tokyo, Japan, and the American cities of San Juan, Puerto Rico; Lake Buena Vista, Florida; Phoenix, Arizona; Scottsdale, Arizona; Anaheim, California; and San Diego, California. The first two rounds had a round-robin format, which led to two teams being eliminated on run difference tiebreakers: in the first round, Canada was eliminated despite its 2–1 record, due to a blowout loss to Mexico as well as failing to run up the score on South Africa; and in the second round, eventual champion Japan advanced despite its 1–2 record, due to a blowout win over Mexico and losing more narrowly to South Korea than did the United States. The higher-seeded teams generally advanced to the second round, including Puerto Rico and Venezuela, as well as the teams mentioned elsewhere in this summary. Although South Korea defeated Japan twice in the earlier rounds, they were matched against each other again in the semifinals as the two teams emerging from the same second round pool, and Japan won that game to advance to the final against Cuba (which had defeated the Dominican Republic in the other semifinal). Japan defeated Cuba 10–6 to be crowned the first champion of the World Baseball Classic. Daisuke Matsuzaka, a Nippon Professional Baseball veteran who was little-known outside Japan at the time, was crowned the Most Valuable Player of the tournament. The following year, he made his debut in the Major Leagues with the Boston Red Sox. FormatThe first World Baseball Classic featured 16 teams in a round-robin. Each team played the other three teams in their pool once. Teams were ranked by winning percentage in the first round, with the top two teams in each pool advancing to the second round, where the teams from Pools A and B (in Pool 1) and the teams from Pools C and D (in Pool 2) competed against each other in another round-robin. Teams were ranked by winning percentage in the second round, without regard to the results of the first round, with the top two teams from each pool entered a four-team single-elimination bracket, with the pool winners and runners-up from each pool facing each other in the semifinals. The winners of the semifinals then met to determine the World Baseball Classic Champions. In the final, the team with the higher winning percentage of games in the tournament were to be the home team. If the teams competing in the final had identical winning percentages in the tournament, then World Baseball Classic, Inc. (WBCI) would conduct a coin flip or draw to determine the home team. In the first two rounds, ties were to be broken in the following order of priority:
RostersEach participating national federation initially submitted a 45-man provisional roster. Final rosters of 28 players, which also must include a minimum of 13 pitchers and two catchers, were later submitted. If a player on the submitted roster was unable to play, usually due to injury, he could be substituted at any time before the start of the tournament. Venues Seven stadiums were used during the tournament:
Pools compositionThe teams selected for the inaugural World Baseball Classic were chosen because they were judged to be the "best baseball-playing nations in the world and provide global representation for the event."[1] There was no official qualifying competition. In addition, there were no world rankings by the International Baseball Federation to determine the strength of the countries.[2][3]
First roundPool A
Pool B
Pool C
Pool D
Source: [citation needed]
Second roundPool 1
Pool 2
Championship round
Semifinals
Semifinal 1 – Cuba 3, Dominican Republic 1
Semifinal 2 – Japan 6, South Korea 0
Final
Final standingsOrganizer WBCI has no interest in the final standings and did not compute. So, it was calculated by IBAF. In the final standings, ties were to be broken in the following order of priority:
Attendance737,112 (avg. 18,900; pct. 67.1%) First round326,629 (avg. 13,610; pct. 55.3%)
Second round283,880 (avg. 23,657; pct. 74.7%)
Championship round126,603 (avg. 42,201; pct. 99.4%)
2006 All-World Baseball Classic teamPlayers named to the All-WBC Team (from left to right); Catcher – Tomoya Satozaki of Japan Third baseman – Adrián Beltré of the Dominican Republic Shortstop – Derek Jeter of the United States Outfielder – Ken Griffey Jr. of the United States Outfielder – Ichiro Suzuki of Japan Pitcher – Chan Ho Park of South Korea
Statistics leaders
Additional rulesThere were several rule changes from normal major league play. Pitchers were held to a pitch count of 65 pitches in the first round, 80 pitches in the second round, and 95 in the championship round. (Netherlands pitcher Shairon Martis used exactly 65 pitches to throw the only no-hitter of the tournament, a 10–0 win over Panama[5] that was stopped by the mercy rule [see below].) If a pitcher reached his maximum pitch count in the middle of an at-bat, he could continue to pitch to that batter, but was required to be replaced once that at-bat ended. A 30–pitch outing needed to be followed by one day off, and a 50–pitch outing by four days off. No one would be allowed to pitch on three consecutive days. A mercy rule came into effect when one team led by either fifteen runs after five innings, or ten runs after seven innings in the first two rounds. In addition, ties could be called after fourteen innings of play. The designated hitter rule was in place for all games. Controversies
South Korea completed the first two rounds undefeated (6-0) but was still forced to play Japan, a team it had already beaten twice, in the semifinal round. South Korea lost the match and subsequently was placed 3rd, despite the fact that South Korea's final standings were 6-1, with the most wins. Other international sporting competitions, such as the FIFA World Cup, are formatted so as to make it impossible for teams to play each other three times. They can only face twice at most – in round robin group play and then again for the championship or 3rd-place match. In addition, the regional grouping of teams was called into question, for the groups were perceived to be unevenly distributed, and the four-team pool system and subsequent three-way tiebreakers were widely seen as awkward.
Tournament organizers were unable to reach an agreement with the MLB umpires' union and so the Classic was overseen by umpires from the minor leagues.
When South Korea beat Japan, they planted South Korean national flags into a pitcher's mound at Angels Stadium at Anaheim.[6]
The Chinese Taipei team was originally listed as "Taiwan" and bearing the ROC national flag, but following pressure from the People's Republic of China the listing was later changed to Chinese Taipei with the Chinese Taipei Olympic flag.
The World Anti-Doping Agency criticized IBAF's drug testing program and threatened to withdraw sanction of the event under claims the MLB was attempting to "brush the issue under the carpet."[7] South Korean pitcher Myung-hwan Park tested positive for a banned substance during the event, and he was subsequently kicked out of the WBC.[1]. Venezuelan pitcher Freddy García tested positive for marijuana.
Numerous MLB players pulled out of the competition for various reasons, such as Barry Bonds,[8] Vladimir Guerrero,[9] and Manny Ramírez,[10] among others. Cuba in particular barred players such as Orlando Hernández, his half-brother Liván Hernández, and José Contreras from its team as Cubans who had previously defected.[11] Success of tournamentMany members of the United States press were skeptical of the Classic since its inception. The event proved to be quite popular, however, providing many memorable moments including a first round game between Venezuela and the Dominican Republic. Attendance was higher than expected at several sites, including the 18,000-seat Hiram Bithorn Stadium in San Juan, which was sold out for every Puerto Rico game in the first two rounds. In addition, there were 4,000 media credentials issued — more than the World Series — which bodes well for the stated goal of internationalizing the sport. Sports Illustrated writer Tom Verducci reported that "more merchandise was sold in the first round than organizers projected for the entire 17-day event." [2] Archived February 24, 2012, at the Wayback Machine He also reported that, at one point, jerseys for the Venezuelan team were selling at the rate of one every six seconds. The U.S. television ratings on ESPN were stronger than initially expected, drawing in more than one million television sets for some games, more than almost any other ESPN program in the month of March. This occurred despite less than stellar airing times for the games. Most were not aired live but taped, and sometimes with innings cut, as the WBC was organized well after ESPN had committed to much of its programming. Outside the U.S. TV ratings were very high. In Latin America, a first-round game between the United States and Mexico, was the third-most-watched game in the history of ESPN Dos, one of the three Spanish-language channels of ESPN in Latin America. The allocation of earningsThe total earnings of the World Baseball Classic is divided into net profit (53%) and prize money (47%).[3] Net profit (53%)
Prize money (47%)
References
External links |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||














