|
Beta Pictoris b
Beta Pictoris b (abbreviated as β Pic b) is an exoplanet orbiting the young debris disk A-type main sequence star Beta Pictoris located approximately 63 light-years (19.4 parsecs, or 6×1014 km) away from Earth in the constellation of Pictor. It has a mass around 13 Jupiter masses and a radius around 46% larger than Jupiter's. It orbits at 9 AU from Beta Pictoris, which is about 3.5 times farther than the orbit of Beta Pictoris c.[4] It orbits close to the plane of the debris disk orbiting the star, with a low eccentricity and a period of 20–21 years. Physical characteristicsMass, radius and temperatureBeta Pictoris b is a super-Jupiter, an exoplanet that has a radius and mass greater than that of the planet Jupiter. It has a temperature of 1,724 K (1,451 °C; 2,644 °F), most likely due to its dusty atmosphere and mass (normally it would be much colder). It has a mass of between 9 and 13 Jupiter masses (MJ),[5] and a radius of 1.46 RJ.[2] In 2018, a study directly measured the astrometric perturbation of Beta Pictoris by Beta Pictoris b, one of the first examples of an exoplanet being measured directly by its astrometric perturbation. Its mass was directly measured as 11±2 MJ.[5] Host starThe planet orbits an (A-type) star named Beta Pictoris. The star has a mass of 1.75 solar masses (M☉) and a radius of 1.8 solar radii (R☉). It has a surface temperature of 8056 K and is 12 million years old. In comparison, the Sun is about 4.6 billion years old[6] and has a surface temperature of 5778 K.[7] It is slightly metal-rich, with a metallicity ([Fe/H]) of 0.06, or 112% of that found in the Sun.[8] Its luminosity (L☉) is 8.7 times that of the Sun. The star's apparent magnitude, or how bright it appears from Earth's perspective, is 3. Therefore, it can be seen with the naked eye. OrbitBeta Pictoris b orbits its host star every 21 years at a distance of 9.2 AU (about the same as Saturn's distance, which is about 9.55 AU). It receives 11% of the amount of sunlight that Earth does from the Sun.[9] The orbit of the planet is well aligned to the rotation of the parent star and debris disk, with misalignment measured to be 3±5 degrees in 2020.[10] Planetary rotationIn 2014, the rotation period of Beta Pictoris b was calculated from the broadening of its carbon monoxide infrared absorption line. This makes it the first extrasolar planet to have its rotation rate measured.[11] With a rotation period of 8.1 hours, it was the fastest-spinning exoplanet known as of 2014.[11][12][13] Its rotation period is faster than that of Jupiter, which has a rotation period of around 10 hours. The rotation period was later refined to 8.7±0.8 hours.[3] DiscoveryThe planet was discovered on November 18, 2008 by Anne-Marie Lagrange et al., using the NACO instrument on the Very Large Telescope at Cerro Paranal in northern Chile.[14] This planet was discovered using the direct imaging technique, using reference star differential imaging. The discovery image was taken in 2003, but the planet was not detected when the data were first reduced. A re-reduction of the data in 2008 using modern image processing tools revealed the faint point source now known to be a planet. Further studiesFollow-up observations performed in late 2009 and early 2010 using the same instrument recovered and confirmed the planet, but on the opposite side of the star. These findings were published in the journal Science[15] and represented the closest orbiting planet to its star ever imaged. Observations performed in late 2010 and early 2011 allowed scientists to establish an inclination angle of the planet's orbit of 88.5 degrees, nearly edge-on. The location of the planet was found to be approximately 3.5 to 4 degrees tilted from the main disk in this system, indicating that the planet is aligned with the warped inner disk in the Beta Pictoris system.[16] The first study of the spectral energy distribution of the planet was published in July 2013.[17] This study shows detections at 1.265, 1.66, 2.18, 3.80, 4.05 and 4.78 μm demonstrating that the planet has a very dusty and/or cloudy atmosphere. The SED is consistent with that of an early L dwarf, but with a lower surface gravity. The effective temperature is constrained to 1700±100 K and the surface gravity to log g = 4.0±0.5. A second study, published in September 2013,[18] provided a new detection at 3.1 μm obtained at the Gemini Observatory along with a reanalysis of previous data. They found the planet to be overluminous in the mid-infrared 3.1 μm band compared to models of early L dwarfs. Models incorporating small dust particles and thick clouds provided the best fit to the SED. The effective temperature is constrained to 1600+50 In 2015, a short video was made from direct images of Beta Pictoris b taken by the Gemini Planet Imager over the course of about two years showing a time-lapse of the planet orbiting around its parent star.[19] It may have been responsible for a transit-like event observed in 1981. In 2018, the PicSat cubesat was launched in a mission to image the planet Beta Pictoris b transiting its host star Beta Pictoris. As of 2022, the orbital parameters and mass of Beta Pictoris b have been measured using a combination of data from radial velocity, astrometry, and imaging,[20] showing that it is about 11.7 times the mass of Jupiter with a semi-major axis of about 10 AU and an orbital period of about 23.6 years.[1] Potential exomoonBeta Pictoris b has been found to have a obliquity likely misaligned by a 2024 study, based on a wide range of simulations together with published measurements. They find that the planet's obliquity must be misaligned if it spins fast, and might be if it spins slow. This misaligment could be caused by collisions with another planets, an unlikely scenario, or secular spin-orbit resonances modified by the presence of an exomoon. An exomoon with a mass similar than that of Neptune, an orbital separation of 0.02–0.05 AU (20–50 planetary radii) and an orbital period ranging from three to seven weeks (20 to 50 days) would induce the largest obliquities, up to 60°.[21] Future observations by the James Webb Space Telescope will measure the planet's obliquity, something never made before in an extrasolar multiplanetary system. A detection of nonzero obliquity could be evidence of an exomoon. Currently the possibility of zero obliquity is unlikely.[21]
Gallery
See alsoNotesReferences
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
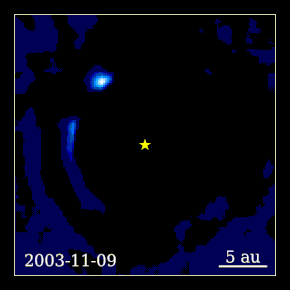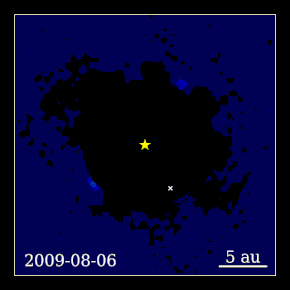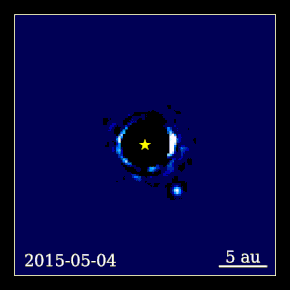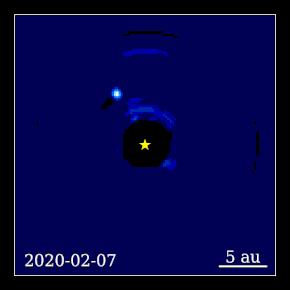
![Beta Pictoris b time-lapse.[22]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b7/Stunning_Exoplanet_Time-lapse_Beta_Pictoris_b.tif/lossy-page1-120px-Stunning_Exoplanet_Time-lapse_Beta_Pictoris_b.tif.jpg)



