|
Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland
The Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland (FPC Church; Scottish Gaelic: An Eaglais Shaor Chlèireach, IPA: [ˈanˈekɫ̪əʃˈhɯːɾˈçleːɾʲəx]) was formed in 1893. The Church identifies itself as the spiritual descendant of the Scottish Reformation. The Church web-site states that it is 'the constitutional heir of the historic Church of Scotland'.[1] Its adherents are occasionally referred to as Seceders or the Wee Wee Frees.[2][3] Although small, the church has congregations on five continents. The Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland is Calvinist in doctrine, worship and practice and the community believes and professes that it accurately practices and adheres to the Word of God: the Bible. The subordinate standard of the church is the Westminster Confession of Faith. History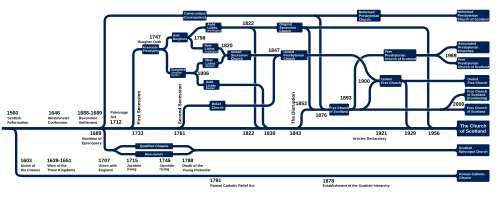 Formation (1893)The founding date of the Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland can be traced to 25 May 1893, when Rev. Donald MacFarlane (1834–1926), who was the Free Church of Scotland minister of Raasay, walked out of the General Assembly in protest. At the 1892 Free Church of Scotland General Assembly, following the example of the United Presbyterian Church of Scotland and the Church of Scotland (1889), the Free Church of Scotland passed a Declaratory Act on 26 May 1892[4] relaxing the stringency of subscription to the Westminster Confession of Faith, which was widely perceived as paving the way for unification with the United Presbyterian Church. Macfarlane was not a member of the 1892 Assembly, but he and his Kirk Session at Kilmallie recorded their protest against it.[5] At the 1893 General Assembly, Macfarlane, who had recently been inducted as pastor of the Raasay congregation, formally protested the Act. The General Assembly rejected his requests and thus confirmed the Act. As a result, he felt compelled to separate himself from the Free Church of Scotland. In this, he was later joined by one other minister, the Rev Donald Macdonald (1825–1901) of Shieldaig. Together they constituted a Presbytery at Raasay on 28 July 1893.[6] GrowthThe result was that a large number of elders and some congregations, mostly in the Highlands, severed their connection with the Free Church of Scotland and formed the Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland, along lines they considered to be more orthodox. By 1907 this body had twenty congregations and twelve ministers. A few years after the Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland was formed (in 1900), the Free Church of Scotland did indeed unite with the United Presbyterian Church of Scotland to form the United Free Church of Scotland, with a somewhat larger minority remaining outside the union and retaining the name Free Church of Scotland. Initially, some wondered if the two churches would merge, but this did not happen, partly because the grounds on which the later separation was based had been the Establishment Principle,[7] rather than the Declaratory Act, which had only been rescinded post separation by the Free Church of Scotland (post 1900). The two denominations took a different view of the 1892 Declaratory Act: the Free Church of Scotland did not regard it as having been a binding measure while the Free Presbyterians did. In 1905, the Free Presbyterian Synod debated proposals for union with the post-1900 Free Church minority. The Synod declared that it would consider union with a church which held ‘the infallibility and inerrancy of the Scriptures of the Old and New Testaments, and the whole doctrine of the Confession of Faith, both in her profession and practice’. The Synod's assessment of the post-1900 Free Church was that ‘although she made ample profession in words’ nevertheless she ‘came far behind in her practice’. One major issue was the Free Church's employment of Professor W. M. Alexander, who had written a book which the FPs and some post-1900 Free Church conservatives believed to be ambiguous about the status of the Bible, as a lecturer in its college. A 1917 Free Church Reply to a FPC Statement of Differences stated underlined the fact that Dr Alexander had in 1905 withdrawn the book from circulation, expressed regret 'for any reflections which the book was fitted to cast on the infallibility of the Word of God' and in 1906 publicly reaffirmed his belief in the inerrancy of Scripture in these words: 'I cherish as more precious than life itself the absolute infallibility of the Word of God'. However a motion was carried at the 1918 FPC Synod which characterized the Reply as containing 'evasive statements and suggestions of compromise'.[8] Some of the Free Presbyterian ministers preferred union with the post-1900 Free Church minority to maintaining a separate Free Presbyterian witness. In 1905 Revs John Macleod (Kames), Alexander Stewart (Edinburgh) and George Mackay (Stornoway) were accepted by the Free Church. In 1918, Revs John R Mackay (Inverness), Alexander Macrae (Portree) and Andrew Sutherland followed suit.[9]  The two denominations are often confused, though not as often as in the past: they were initially of a predominantly Highland background, continue to share support for the Westminster Confession of Faith, and express a socially conservative outlook. However, the Free Presbyterian Church considers it a sin to use public transport to go to church on the Sabbath,[10] while the Free Church does not. The Free Church permits the use of modern Bible translations, while the Free Presbyterian Church prescribes the exclusive use of the Authorized Version in public worship (by resolution of the Synod in 1961[11]), and as the only version recommended for use in family and private devotions. Split in 1989In 1989, a splinter group formed the Associated Presbyterian Churches "following the perceived failure of the Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland to put into practice chapters 20 and 26 of the Westminster Confession of Faith",[12] following the suspension of Lord Advocate and Lord Chancellor Lord Mackay of Clashfern as an elder for attending the Roman Catholic Requiem Masses offered for two of his deceased fellow judges. The Moderator of Synod at the time was a minister from Zimbabwe, the late Aaron Ndebele, an Ndebele. The FPC continues to oppose many aspects of the Catholic Church, including Mass, and has protested from time to time against figures in positions of authority including the British Royal Family attending Mass. It wrote to Prince Charles to complain of his presence at a requiem mass for one of his cousins in 2013.[13] The church maintains that the Pope is the Antichrist.[14] Disunity in the Scottish Reformed church sceneThe Free Presbyterians believe that the denominations in Scotland adhering to the Westminster Confession of Faith should unite with it after repentance over historical retreat from the Confession. The FPC Catechism (the 2013 edition is an updated version of the original 1942-1943 edition) says: 'All Presbyterian Churches in Scotland claiming to represent the Reformed Church and who have caused or who maintain schisms contrary to the avowed Westminster Standards are bound to repent and to return to purity in doctrine, worship, government and discipline. The Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland is not guilty of schism and claims to be the true heir of the Reformed Church of Scotland in doctrine, worship, government and discipline. While she certainly does not claim perfection, she maintains that all churches in Scotland should unite around her constitution and testimony'.[15] Twenty-first century developmentsChurch extension work tends to be low-key and results to be measured in the long-term in the Free Presbyterian Church. It stresses the need for the Holy Spirit to work in the soul before any spiritual life will be present, the need for the church to provide Bible-based and Christ-focused preaching, emphasizes the need for a holy life by those who claim conversion, and encourages example as well as precept in evangelism. It has not emulated other evangelical churches in their approach to reaching the secular UK. Its Catechism explains: 'Many modern churches have drama, dancing, and music bands in their worship and use sport and social entertainment to attract and retain young people; but these things are of the world and should not be countenanced by the Church of Christ for promoting the interests of the kingdom'.[16] Public pronouncements about the current state of the nation tend to combine concern about Free Presbyterian spiritual decline with fears of increased secularization of other Reformed churches. A 2014 report to the FP Religion and Morals Committee quoted from a FP Outer Isles presbytery report, but said the issues were relevant for many other parts of the country. 'We must acknowledge the low state of religion among ourselves' it said, adding of other denominations: '...we find that many professing Christians in the Churches are actively encouraged to continue their former worldly interest in professional and amateur sport, worldly music, entertainments such as the cinema, dances, use of public houses, concerts and ceilidhs, and that many speak and dress like the world with little distinction to be found between them and their former companions'.[17] Moderators of SynodUnlike the Church of Scotland and Free Church of Scotland, the annual meeting to consider the progress and direction of the church is called a Synod rather than a General Assembly. Synods are not in any particular fixed months (and may occur more than once per year) and ministers may serve as Moderator more than once. Known Moderators are:[18][19]
PresbyteriesThe individual churches[20] of the Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland are each part of[21] one of six[22] Presbyteries. Presbyteries meet regularly, and all Presbyteries meet at the yearly Synod in May. Asia Pacific PresbyteryThe Asia Pacific Presbytery covers Australia, New Zealand and Singapore. The congregations in Australia[23] are found on the East Coast: one in Grafton (received 1911),[24] and one in Sydney.[25] The congregations in New Zealand are all on the North Island: Auckland,[26] Gisborne (founded 1954), Tauranga, and Carterton. There is one congregation in Singapore (received 2000). Northern PresbyteryThe Northern Presbytery[27] comprises the congregations Inverness, Dingwall, and Aberdeen among others. Outer Isles PresbyteryThe Outer Isles Presbytery consists of the congregations on the Outer Hebrides. Southern PresbyteryThe Southern Presbytery[28] consists of the Scottish congregations South of the Scottish Highlands, and the congregations in England and North America. There is one congregation in London (founded 1898). There is one congregation in Canada, in Chesley, Ontario (founded 1902).[29] In the United States there is one congregation, in Santa Fe, Texas (received 2000).[30] Western and Skye PresbyteryThe Western and Skye Presbytery[31] consists of the Western parts of Scotland including Skye, but also the congregation in Odesa,[32] in Ukraine (received 2002). Zimbabwe PresbyteryIn Zimbabwe services are held in forty locations[33] with their centres in Bulawayo, Ingwenya, Mbuma, New Canaan and Zenka. The Zimbabwe mission began in 1904. List of congregations in the UK
References
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Free Presbyterian Church of Scotland. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
















