|
Gasoline and diesel usage and pricing
 The usage and pricing of gasoline (or petrol) results from factors such as crude oil prices, processing and distribution costs, local demand, the strength of local currencies, local taxation or subsidy, and the availability of local sources of gasoline (supply). Since fuels are traded worldwide, the trade prices are similar.[citation needed] The price paid by consumers largely reflects national pricing policy. Most countries impose taxes on gasoline (petrol), which causes air pollution and climate change; whereas a few, such as Venezuela, subsidize the cost.[1] Some country's taxes do not cover all the negative externalities, that is they do not make the polluter pay the full cost.[2][3][4] Western countries have among the highest usage rates per person. The largest consumer is the United States.[5] Fuel prices in the United States
  In 2008, a report by Cambridge Energy Research Associates stated that 2007 had been the year of peak gasoline usage in the United States, and that record energy prices would cause an "enduring shift" in energy consumption practices.[6] According to the report, in April fuel consumption had been lower than a year before for the sixth straight month, suggesting 2008 would be the first year US usage declined in 17 years. The total annual distance driven in the US began declining in 2006.[7] After Hurricane Katrina and Hurricane Rita, gas prices started rising to record high levels. In terms of the aggregate economy, increases in crude oil prices significantly predict the growth of real gross domestic product (GDP), but increases in natural gas prices do not.[8] In August 2005, after the damages from Hurricane Katrina ran up gas prices, on August 30, a day after Katrina's landfall, prices in the spot market, which typically include a premium above the wellhead price, had surged past $11 per gigajoule ($12 per million British thermal units), and on 22 September 2005, the day before Rita's landfall, the spot price had risen to $14 per gigajoule ($15 per million British thermal units).[8] In the fifteen years prior to the 1973 oil crisis, gasoline prices in the U.S. had lagged well behind inflation.[9] A 249-page May 2004 report by the Government Accountability Office (GAO)—the "congressional watchdog", investigating the impact of about 2,600 petroleum industry mergers from the 1990s to 2004, said that one of the consequences of the mergers was that they enhanced the ability for the merged companies to control prices.[10] Companies engaged in exploration and production were more likely to merge to improve efficiency and to decrease costs.[10] In early 2020 the gas price has dropped down to a national average of $1.73 a gallon.[11] In 2021, the average price increased to $3.01/gallon.[12] By the end of June 2022, the price of gasoline reached a record high of over $5/gallon with some places reporting $6/gallon.[13] While prices have come down since the peak in June, prices were beginning to tick up again. Gas prices hit $3.79 a gallon the week of September 29, 2022, up from $3.73 on September 23, 2022 — an increase of $0.06 per gallon over the last week.[14] Since October 10, 2022, the price of gasoline has gone down again. Gas prices dropped down to $3.64 a gallon by November 28, 2022, down from $3.76 the week before – a decrease of $0.11 per gallon during that time. Factors affecting gasoline pricesAccording to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), as of March 2022, factors that affect the price of gasoline in the United States include the price of crude oil per barrel, costs and profits related to refining, distribution, and marketing, and taxes, along with the charge set by refiners for gasoline based on based on octane levels, with higher octane levels—premium grade cost about 68 cents per gallon more than regular grade in 2021.[12] The largest component of the average price of $2.80/gallon of regular grade gasoline in the United States from 2012 through 2021, representing 54.8% of the price of gas, was the price of crude oil. The second largest component during the same period was taxes—federal and state taxes representing 17% of the price of gas. The third component, representing 14.3% was distribution and marketing. The fourth component representing 14% was refining costs and profits. In 2021, with the average price increased to $3.01/gallon, crude oil accounted for 53.6%, taxes for 16.4%, distribution and marketing for 15.6%, and refining costs and profits, for 14.4%.[12] Crude oilCrude oil is the greatest contributing factor when it comes to the price of gasoline and diesel.[12] This includes the resources it takes for exploration, to remove it from the ground, and transport it. Between 2004 and 2008, there was an increase in fuel costs due in large part to a worldwide increase in demand for crude oil. Prices leapt from $35 to $140 per barrel ($220 to $880/m3), causing a corresponding increase in gas prices.[15] On the supply side, OPEC (or the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) has a great deal to do with the price of gasoline, both in the United States and around the world. The speculation of oil commodities can also affect the gasoline market. Marketing and distributionDistribution and marketing makes up the remaining 5%. The price of transporting crude oil to a refinery then gasoline to a point of distribution is passed on to the consumer. In addition the price to market the fuel brand is passed on. Taxes Federal Taxes State Taxes Other factorsAside from this breakdown, many other factors affect gasoline prices. Extreme weather, war or natural disaster in areas where oil is produced can also in turn raise the price of a gallon of gasoline. Legislation by several states for cleaner burning fuel also affects certain areas' prices of gasoline. Balance between supply and demand directly affects the price of gasoline. U.S. consumption of gasoline follows a seasonal pattern, where every year it is more expensive during the summer months when more people are driving. The long-term trend of consumption has been to increase year over year since 1950, with dips around the introduction of corporate average fuel economy standards and the 1979 energy crisis, the early 1990s recession and Gulf War, and the Great Depression.[19] Petrol usage and pricing in Europe Most European countries have higher fuel taxes than the US, but Russia and some neighboring countries have a much smaller tax, with fuel prices similar to the US.[1] Competitive petrol pricing in the UK is led by supermarkets with their own forecourts. Generally each supermarket tends to match the other's prices; the lead players being Asda, Tesco, Sainsbury's and Morrisons.[20] Countries with subsidised gasolineA number of countries subsidize fossil fuels such as petrol/gasoline and other petroleum products. Subsidies make transport of people and goods cheaper, but discourage fuel efficiency. In some countries, the soaring cost of crude oil since 2003 has led to these subsidies being cut, moving inflation from the government debt to the general populace, sometimes resulting in political unrest. Fuel subsidies are common in oil-rich nations. Countries with subsidized fuel include Saudi Arabia, Iran, Egypt, Burma, Kuwait, Bahrain, Trinidad and Tobago, Brunei, Venezuela, Ecuador and Bolivia.[citation needed] In February 2010, the Iranian government implemented an energy price reform by which the energy subsidies were to be removed in five years; the most important price hike was in gasoline, as the price went up from 1000 rials ($0.10 US) to 4000 rials ($0.40 US) per litre, with a ration of 100 litres per month for private passenger cars (later reduced to 60 litres per month). On 26 December 2010, the Bolivian government issued a decree removing subsidies which had fixed petrol/gasoline and diesel prices for the past seven years. Arguing that illegal exports (contraband) of gasoline and diesel fuel to neighboring countries by individuals for personal profit was harming the economy, Bolivia eliminated the subsidies and raised gasoline prices as much as 83%. After widespread labor strikes, the Bolivian government canceled all future planned price hikes.[21] Venezuela used to have the cheapest gasoline in the world for decades, however on 19 February 2016 president Nicolás Maduro used decree powers to raise fuel prices by 6000%. This was the first rise in petrol prices in 20 years and he also set in place a sharp devaluation of the currency which he said aimed to shore up the country's failing economy, hard hit by falling oil prices which make up 95% of foreign income. Prices at the pump in Venezuela jumped as much as 6,086% for 95 octane gasoline, from 0.097 bolivars to 6 bolivars.[22] May 20, 2020 government increased the price to US$0.5 a litre. IranThe Iranian government introduced an energy price reform in February 2010. The reform was brought forward by the government and approved with some changes by the parliament. The major aim of the policy was to slow down the increasing trend of energy consumption in Iran by removing the energy subsidies. The plan included electricity, natural gas, gasoline, and diesel subsidies. According to the plan, all energy prices were to increase by 20 percent annually. The price reform was particularly important in gasoline, as consumption had been increasing dramatically creating a huge burden on government budget. Furthermore, to meet demand, Iran had to import gasoline from other countries, which made the country vulnerable to possible sanctions by the US and European countries. The gas price prior to reform was $0.10 US per liter with the quota of 100 liters per month per passenger car. The reform raised the price to $0.40 US per liter and later reduced the ration to 60 liters per month. The price for over-quota consumption and the imported cars were $0.70 US per liter. The energy price reform included a cash-rebate program through which each person received 455,000 rials ($15 US) per month from the government. The overall consumption of gasoline after the reform decreased from about 65 million liters per day to about 54 million liters per day.[23] The price of gasoline based on the official USD to IRR rate is US$0.29/Litre in 2018 which is the second cheapest price in the world after Venezuela.[24] NigeriaPetrol subsidies mainly benefit rich people.[25] On 1 January 2012, the Nigerian government headed by president Goodluck Ebele Jonathan, tried to cease the subsidy on petrol and deregulate the oil prices by announcing the new price for petrol as US$0.88/litre from the old subsidised price of US$0.406/litre (LAGOS), which in areas distant from Lagos petrol was priced at US$1.25/litre. This led to the longest general strike (eight days), riots, Arab spring like protests and on 16 January 2012 the government capitulated by announcing a new price of US$0.60/litre with an envisaged price of US$2.0/litre in distant areas.[26] In May 2016 the Buhari administration increased fuel prices again to NGN 145 per litre ($0.43 at black market rates for the currency).[27] In September 2020, the government had announced an increase in the pump price of petrol to NGN 151.56 per litre from NGN 148.[28] MexicoPEMEX, a government company in charge of selling oil in Mexico is subsidized by the Mexican government. This serves to quell inflationary pressures in Mexico. Mexico buys much of its gasoline and diesel from the United States and resells it at US$98 per barrel. Many residents of US border communities cross the border to buy fuel in Mexico,[29] thereby enjoying a cheaper fuel subsidy at the expense of Mexican taxpayers. This has caused frequent supply shortages at a number of filling stations along the border for Mexican drivers, especially truck and bus drivers who use diesel.[30] In 2017, Mexico ended its oil industry subsidies, leading to increased prices and widespread protests throughout the country.[31] Trinidad and TobagoTrinidad and Tobago through its national energy agencies Petrotrin and Trinidad and Tobago National Petroleum Marketing Company Limited (NP)[32] offers petroleum fuels at varying subsidised prices to the users within the country.[33] Unleaded Gasoline is offered at two grades - Ron 91 at US$0.43/Litre and Ron 95 at US$0.91/Litre. Diesel is offered at US$0.24/Litre making this fuel some of the cheapest in the world. There are an estimated 791,086 cars in the country as at February 2015 and they consume 1.2 billion litres of liquid fuel annually The Government of Trinidad and Tobago spent an estimated US$173.2 million in subsidies for gasoline and diesel in half year period October 2014 - March 2015.[34] United States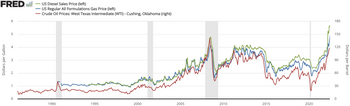 Diesel fuel (Left) Gasoline (Left) Crude Oil Price (WTI) (Right) The oil industry receives subsidies through the United States tax code, which include Percentage Depletion Allowance,[35] Domestic Manufacturing Tax Deduction, the Foreign Tax Credit and Expensing Intangible Drilling Costs. It is estimated that these tax deductions are worth $4 billion annually and are currently being debated by the government for reform.[citation needed] Although such subsidies exist, the sale of fuel is also taxed at rates that far exceed the sales tax rates for other goods, to help pay for bridge and road repair. It is thus unclear whether the tax impact on fuel is a net subsidy or not. However, fuel taxes can account for less than half of government road and highway spending. The additional spending is clearly a subsidy, since the existence of these roads creates fuel demand. Moreover, since the fuel tax itself is allocated to road repair, and petroleum vehicles are the main users of roads, one cannot claim the existence of such a tax cancels out other subsidies.
In 2021-22, gasoline and diesel prices surged in the United States, reaching record highs, as part of a larger trend of inflation.[36] The average price of regular gasoline rose from $1.773 during the week of April 27, 2020, to $5 as of June 11, 2022, an all-time high.[37] California led the nation in gas prices with an average gallon of regular gas in the state reaching $6.43 as of June 11, 2022.[38] VenezuelaCurrently, in Venezuela, there are a total of 1,500 gas stations. 500 of these gas stations sell gas for the subsidized price, 500 sell gas at a dollar price, and the rest sell gas interchangeably between both (subsidized & unsubsidized). In 2013, PDVSA, Venezuelan state-owned company, spent US$1.7 billion in direct costs of importation of gasoline, and subsidizing all sales of gasoline in the internal Venezuelan market. The sale price of gasoline was US$0.015[needs update] per liter, on a fixed price in the local currency that has been in effect since 1997. Given the low price of gasoline, it is distributed free of charge to gas stations.[39] On May 30, 2020, government did announce a price increase to US$0.5 per liter which is the price until now Jun 4 2021, but with supply shortages at the service stations. Countries that formerly subsidised gasolineIndonesiaWith oil reaching over US$145 a barrel, Indonesia further increased prices in May 2008 to Rp 6,000 (approx. US$0.65) per litre, and diesel to Rp 5,500 (approx. US$0.60) per litre, while kerosene was raised to Rp 2,500 (approx. US$0.28), moves which caused widespread protests.[40] Furthermore, in November 2014, the new government led by President Joko Widodo reallocated the government subsidy for gasoline and diesel into nation's infrastructure, education and health budget, hence raised the price of subsidized gasoline and diesel by Rp 2,000 each, so the price of gasoline and diesel became Rp 8,500 and Rp 7,500 respectively. This decision created inflation and protest throughout the archipelago.[41] MalaysiaMalaysia had been subsidising gasoline since 1983.[42] In 2014, Malaysia abolished fuel subsidies and began using a managed float system, in order to control the country's large current account deficit.[43][44] Gasoline prices around the world
ProtestsIndiaWide protests on petrol price hikes have been frequent in the last decade.[when?][citation needed] On 24 May 2012, the petrol price was hiked by ₹7.50, resulting prices in the range of ₹73–82 ($0.97–1.09) per liter all over the country.[58] Opposition had declared a bandh on 31 May 2012 across the country to protest against the price hike,[59] which evoked mixed response amid incidents of stone pelting, arson and road blockades in some parts of the country.[60][61] See alsoReferences
External linksUnited States
International
|


