|
Henry reaction
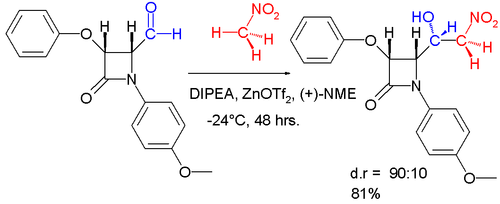
The Henry reaction is a classic carbon–carbon bond formation reaction in organic chemistry. Discovered in 1895 by the Belgian chemist Louis Henry (1834–1913), it is the combination of a nitroalkane and an aldehyde or ketone in the presence of a base to form β-nitro alcohols.[1][2][3] This type of reaction is also referred to as a nitroaldol reaction (nitroalkane, aldehyde, and alcohol). It is nearly analogous to the aldol reaction that had been discovered 23 years prior that couples two carbonyl compounds to form β-hydroxy carbonyl compounds known as "aldols" (aldehyde and alcohol).[2][4] The Henry reaction is a useful technique in the area of organic chemistry due to the synthetic utility of its corresponding products, as they can be easily converted to other useful synthetic intermediates. These conversions include subsequent dehydration to yield nitroalkenes, oxidation of the secondary alcohol to yield α-nitro ketones, or reduction of the nitro group to yield β-amino alcohols.  Many of these uses have been exemplified in the syntheses of various pharmaceuticals including the β-blocker (S)-propranolol,[5][6] the HIV protease inhibitor Amprenavir (Vertex 478), and construction of the carbohydrate subunit of the anthracycline class of antibiotics, L-Acosamine.[6] The synthetic scheme of the L-Acosamine synthesis can be found in the Examples section of this article. MechanismThe Henry reaction begins with the deprotonation of the nitroalkane on the α-carbon position forming a nitronate. The pKa of most nitroalkanes is approximately 17.[7][8] Although this structure is nucleophilic both at the deprotonated carbon and at the oxy-anions of the nitro group,[9] the observed result is of the carbon attacking the carbonyl compound. The resulting β-nitro alkoxide is protonated by the conjugate acid of the base that originally deprotonated the nitroalkyl structure, giving the respective β-nitro alcohol as product.  All steps of the Henry reaction are reversible. This is due to the lack of a committed step in the reaction to form product. It is for this reason that research has been geared towards modifications to drive the reaction to completion.[2][3] More information about this can be found in the modification section of this article. Stereochemical CourseThe figure below illustrates one of the commonly accepted models for stereoselection without any modification to the Henry reaction. In this model, stereoselectivity is governed by the size of the R groups in the model (such as a carbon chain), as well as by a transition state that minimizes dipole by orienting the nitro group and carbonyl oxygen anti each other (on opposite sides of the molecule). The R groups play a role in the transition state of the Henry reaction: the larger the R groups on each of the substrates, the more they will tend to orient themselves away from each other (commonly referred to as steric effects). [3][10] 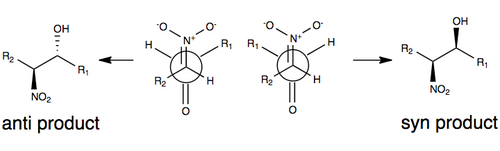 Due to the reversibility of the reaction and the tendency for easy epimerization of the nitro-substituted carbon atom (among a number of factors), the Henry reaction will typically produce a mixture of enantiomers or diastereomers. It is for this reason that explanations for stereoselectivity remain scarce without some modification of the reaction.[3] In recent years, research focus has shifted toward modifications of the Henry reaction to overcome this synthetic challenge.  The first example of an enantioselective nitroaldol reaction was reported in 1992 using Shibasaki catalysts.[11] One of the most frequently employed methods for inducing enantio- or diastereoselectivity in the Henry reaction is the use of chiral metal catalysts, in which the nitro group and carbonyl oxygen coordinate to a metal that is bound to a chiral organic molecule. Some metals that have been used include zinc, cobalt, copper, magnesium, and chromium.[12] A depiction of this coordination is illustrated above. General FeaturesOne of the many features of the Henry reaction that makes it synthetically attractive is that it utilizes only a catalytic amount of base to drive the reaction. Additionally a variety of bases can be used including ionic bases such as alkali metal hydroxides, alkoxides, carbonates, and sources of fluoride anion (e.g. TBAF) or nonionic organic amine bases including TMG, DBU, DBN, and PAP. The base and solvent used do not have a large influence on the overall outcome of the reaction.[2] LimitationsOne of the main drawbacks of the Henry reaction is the potential for side reactions throughout. Aside from the inherent reversibility of the reaction (or "retro–Henry") that can prevent the reaction from proceeding, the β-nitro alcohol also has the potential to undergo dehydration. For sterically hindered substrates, it is also possible for a base-catalyzed self-condensation (Cannizzaro reaction) to occur. A general scheme of the Cannizzaro reaction is depicted below.[2]  ModificationsThere have been a series of modifications made to the Henry reaction. Of these some of the most important include employing high-pressure and sometimes solvent free conditions to improve chemo- and regioselectivity[2] and chiral metal catalysts to induce enantio-or diastereoselectivity.[12] The aza-Henry reaction is also used to produce nitroamines and can be a reliable synthetic route for the synthesis of vicinal diamines.[13] Perhaps one of the most synthetically useful modifications to the Henry reaction is the use of an organocatalyst.[2][12][14] The catalytic cycle is shown below.  Benjamin List described that while this is a broad explanation, his brief review illustrates that this is a plausible mechanistic explanation for almost all reactions that involve an organocatalyst. An example of this type of reaction is illustrated in the Examples section of this article. In addition to the previously mentioned modifications to the Henry reaction there are a variety of others. This includes the conversion of unreactive alkyl nitro compounds to their corresponding dianions which will react faster with carbonyl substrates, reactions can be accelerated using PAP as base, utilization of the reactivity of aldehydes with α,α-doubly deprotonated nitroalkanes to give nitronate alkoxides that yield mainly syn-nitro alcohols once protonated, and finally generation of nitronate anions in which one oxygenatom on the nitro group is silyl-protected to yield anti-β-nitro alcohols in the presence of a fluoride anion source when reacted with an aldehyde.[2][3] Examples
References
External links
|
||||||||||||||||