|
Liptó County
Liptó County (Hungarian: Liptó vármegye, Latin: Comitatus Liptoviensis, Slovak: Liptovská župa, German: Komitat Liptau, Polish: Komitat Liptów) was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in northern Slovakia. Geography  Liptó county shared borders with the Austrian land Galicia and the Hungarian counties Árva, Turóc, Zólyom, Gömör-Kishont and Szepes. The county's territory was situated along the upper Vág (present-day Váh) river between the High Tatras and the Low Tatras. Its area was 2,247 km2 around 1910. Today, the territory of the former Liptó County largely corresponds to the Ružomberok District and Liptovský Mikuláš District in northern Slovakia. Three villages (Liptovská Teplička, Štrba and Štrbské Pleso) are now in the Poprad District. CapitalsThe capitals of the county were the Liptó Castle, later Németlipcse (present-day Partizánska Ľupča), and since 1677 the capital was Liptószentmiklós (present-day Liptovský Mikuláš). HistoryLiptó county as a Hungarian comitatus arose before the 15th century. At various points throughout history the county was ruled by Voivodes or Counts from the Rosenberg, Csák and Benyovszky families. In the aftermath of World War I, the area became part of newly formed Czechoslovakia, as recognized by the concerned states in 1920 by the Treaty of Trianon. Demographics
Subdivisions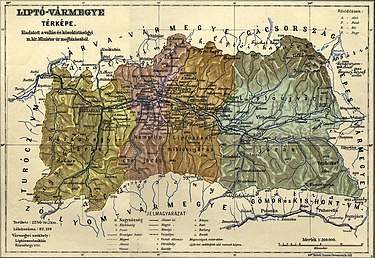 In the early 20th century, the subdivisions of Liptó County were:
NotesReferences
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


