|
Onyx River
The Onyx River is an Antarctic meltwater stream which flows westward through the Wright Valley from Wright Lower Glacier and Lake Brownworth at the foot of the glacier to Lake Vanda, during the few months of the Antarctic summer. At 32 kilometres (20 mi) in length, it is the longest river in Antarctica.[1] Geography The Onyx River flows away from the ocean, an example of endorheic drainage, as the Wright Lower Glacier blocks the mouth of the Wright Valley. It has several tributaries, and there are multiple meteorological stations along the length of the river. Flow levels are highly variable, both during the day and between summers, with the river failing to reach the lake some years. In contrast, it can cause significant erosion in flood years, and was rafted in 1984 by New Zealand researchers. At one time, the river's discharge reached 20 cubic metres per second (700 cu ft/s).[2] EnvironmentThere are no fish in the Onyx River, but it supports microscopic life, and the algal blooms can be quite extensive. The environment consists mainly of cyanobacteria and other algae. A few micro-animals (nematodes, tardigrades, and rotifers) live in the river. Skuas are also occasionally present in the area.[3] MonitoringThe Onyx River is one of the many sites studied by the United States Antarctic Program of the National Science Foundation. Discharge data has been collected at the downstream gauge near Lake Vanda since 1969 and at the upstream gauge near the Wright Lower Glacier since 1972.[4] The Antarctica New Zealand program once maintained a semi-permanent camp at Lake Vanda which has since been removed. NSF's McMurdo Long Term Ecological Research site has been maintaining the Onyx River record since 1993. There is a small research shelter at Lake Vanda at its eastern end. Nearby is the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Seismic station at Bull Pass. Since records have been kept, the Onyx River's flow season has shifted earlier and become longer.[4] 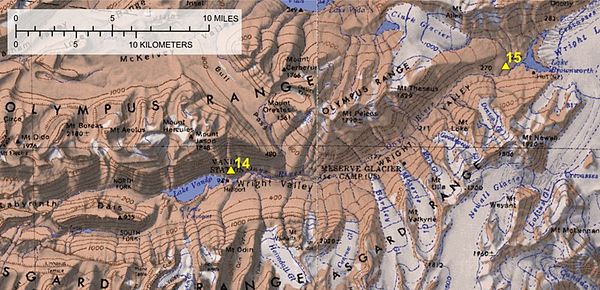 See alsoReferences
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||

