|
Ottawa dialect
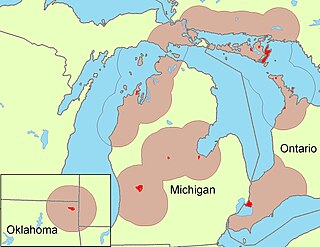
Ottawa or Odawa is a dialect of the Ojibwe language spoken by the Odawa people in southern Ontario in Canada, and northern Michigan in the United States. Descendants of migrant Ottawa speakers live in Kansas and Oklahoma. The first recorded meeting of Ottawa speakers and Europeans occurred in 1615 when a party of Ottawas encountered explorer Samuel de Champlain on the north shore of Georgian Bay. Ottawa is written in an alphabetic system using Latin letters, and is known to its speakers as Nishnaabemwin 'speaking the native language' or Daawaamwin 'speaking Ottawa'. Ottawa is one of the Ojibwe dialects that has undergone the most language change, although it shares many features with other dialects. The most distinctive change is a pervasive pattern of vowel syncope that deletes short vowels in many words, resulting in significant changes in their pronunciation. This and other innovations in pronunciation, in addition to changes in word structure and vocabulary, differentiate Ottawa from other dialects of Ojibwe. Like other Ojibwe dialects, Ottawa grammar includes animate and inanimate noun gender, subclasses of verbs that are dependent upon gender, combinations of prefixes and suffixes that are connected with particular verb subclasses, and complex patterns of word formation. Ottawa distinguishes two types of third person in sentences: proximate, indicating a noun phrase that is emphasized in the discourse, and obviative, indicating a less prominent noun phrase. Ottawa has a relatively flexible word order compared with languages such as English. Ottawa speakers are concerned that their language is endangered as the use of English increases and the number of fluent speakers declines. Language revitalization efforts include second language learning in primary and secondary schools. ClassificationOttawa is known to its speakers as Nishnaabemwin 'speaking the native language' (from Anishinaabe 'native person' + verb suffix -mo 'speak a language' + suffix -win 'nominalizer', with regular deletion of short vowels); the same term is applied to the Eastern Ojibwe dialect.[4] The corresponding term in other dialects is Anishinaabemowin.[5] Daawaamwin (from Odaawaa 'Ottawa' + verb suffix -mo 'speak a language' + suffix -win 'nominalizer', with regular deletion of short vowels) 'speaking Ottawa' is also reported in some sources.[6] The name of the Canadian capital Ottawa is a loanword that comes through French from odaawaa, the self-designation of the Ottawa people.[7][8] The earliest recorded form is Outaouan, in a French source from 1641.[9] Ottawa is a dialect of the Ojibwe language, which is a member of the Algonquian language family.[10] The varieties of Ojibwe form a dialect continuum, a series of adjacent dialects spoken primarily in the area surrounding the Great Lakes as well as in the Canadian provinces of Quebec, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan, with smaller outlying groups in North Dakota, Montana, Alberta, and British Columbia. Mutual intelligibility is the linguistic criterion used to distinguish languages from dialects.[11][12] In straightforward cases, varieties of language that are mutually intelligible are classified as dialects, while varieties of speech that are not mutually intelligible are classified as separate languages.[13] Linguistic and social factors may result in inconsistencies in how the terms language and dialect are used.[14] Languages spoken in a series of dialects occupying adjacent territory form a dialect continuum or language complex, with some of the dialects being mutually intelligible while others are not. Adjacent dialects typically have relatively high degrees of mutual intelligibility, but the degree of mutual intelligibility between nonadjacent dialects varies considerably. In some cases, speakers of nonadjacent dialects may not understand each other's speech.[14][15] A survey conducted during the 1980s and 1990s found that the differences between Ottawa, the Severn Ojibwe dialect spoken in northwestern Ontario and northern Manitoba, and the Algonquin dialect spoken in western Quebec result in low levels of mutual intelligibility.[16] These three dialects "show many distinct features, which suggest periods of relative isolation from other varieties of Ojibwe."[17] Because the dialects of Ojibwe are at least partly mutually intelligible, Ojibwe is conventionally considered to be a single language with a series of adjacent dialects.[18] Taking account of the low mutual intelligibility of the most strongly differentiated dialects, an alternative view is that Ojibwe "could be said to consist of several languages",[18] forming a language complex.[19] Geographic distributionThe Ottawa communities for which the most detailed linguistic information has been collected are in Ontario. Extensive research has been conducted with speakers from Walpole Island in southwestern Ontario near Detroit, and Wikwemikong on Manitoulin Island in Lake Huron. South of Manitoulin Island on the Bruce Peninsula are Cape Croker and Saugeen, for which less information is available.[20] The dialect affiliation of several communities east of Lake Huron remains uncertain. Although "the dialect spoken along the eastern shore of Georgian Bay" has been described as Eastern Ojibwe, studies do not clearly delimit the boundary between Ottawa and Eastern Ojibwe.[21][16][22] Other Canadian communities in the Ottawa-speaking area extend from Sault Ste Marie, Ontario along the north shore of Lake Huron: Garden River,[23] Thessalon,[24] Mississauga (Mississagi River 8 Reserve,[25][26] Serpent River,[27][28] Whitefish River,[24][29] Mattagami,[25] and Whitefish Lake.[24] In addition to Wikwemikong, Ottawa communities on Manitoulin Island are, west to east: Cockburn Island,[30] Sheshegwaning,[27][31] West Bay,[24] Sucker Creek,[24][32] and Sheguiandah.[27][33] Other Ottawa communities in southwestern Ontario in addition to Walpole Island are: Sarnia, Stoney and Kettle Point, and Caradoc (Chippewas of the Thames), near London, Ontario.[34][35] Communities in Michigan where Ottawa linguistic data has been collected include Peshawbestown, Harbor Springs, Grand Rapids, Mount Pleasant, Bay City, and Cross Village.[34][36] The descendants of migrant Ottawas live in Kansas and Oklahoma;[37][38] available information indicates only three elderly speakers in Oklahoma as of 2006.[39] Reliable data on the total number of Ottawa speakers is not available, in part because Canadian census data does not identify the Ottawa as a separate group.[40] One report suggests a total of approximately 8,000 speakers of Ottawa in the northern United States and southern Ontario out of an estimated total population of 60,000.[41] A field study conducted during the 1990s in Ottawa communities indicates that Ottawa is in decline, noting that "Today too few children are learning Nishnaabemwin as their first language, and in some communities where the language was traditionally spoken, the number of speakers is very small."[42] Formal second-language classes attempt to reduce the impact of declining first-language acquisition of Ottawa.[43] Population movementsAt the time of first contact with Europeans in the early 17th century, Ottawa speakers resided on Manitoulin Island, the Bruce Peninsula, and probably the north and east shores of Georgian Bay. The northern area of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan has also been a central area for Ottawa speakers since the arrival of Europeans.[44] Since the arrival of Europeans, the population movements of Ottawa speakers have been complex,[44] with extensive migrations and contact with other Ojibwe groups.[45] Many Ottawa speakers in southern Ontario are descended from speakers of the Southwestern Ojibwe dialect (also known as "Chippewa") who moved into Ottawa-speaking areas during the mid-19th century. Ottawa today is sometimes referred to as Chippewa or Ojibwe by speakers in these areas.[36] As part of a series of population displacements during the same period, an estimated two thousand American Potawatomi speakers from Wisconsin, Michigan and Indiana moved into Ottawa communities in southwestern Ontario.[46] The non-Ottawa-speaking Ojibwes who moved to these areas shifted to speaking Ottawa, as did the Potawatomi migrants. As a result of the migrations, Ottawa came to include Potawatomi and Ojibwe loanwords.[47] Two subdialects of Ottawa arise from these population movements and the subsequent language shift. The subdialects are associated with the ancestry of significant increments of the populations in particular communities and differences in the way the language is named in those locations.[48] On Manitoulin Island, where the population is predominantly of Ottawa origin, the language is called Ottawa, and has features that set it off from other communities that have significant populations of Southwestern Ojibwe (Chippewa) and Potawatomi descent. In the latter communities, the language is called Chippewa but is still clearly Ottawa. Dialect features found in "Ottawa Ottawa" that distinguish it from "Chippewa Ottawa" include deletion of the sounds w and y between vowels, glottalization of w before consonants,[49] changes in vowel quality adjacent to w,[50] and distinctive intonation.[48][51] PhonologyOttawa has seventeen consonants and seven oral vowels; there are also long nasal vowels whose phonological status is unclear.[52] In this article, Ottawa words are written in the modern orthography described below, with phonetic transcriptions in brackets using the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) as needed.[53] The most prominent feature of Ottawa phonology is vowel syncope, in which short vowels are deleted, or in certain circumstances reduced to schwa [ə], when they appear in metrically defined weak syllables. Notable effects of syncope are:[54]
ConsonantsThe table of consonants uses symbols from the modern orthography with the corresponding symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) following where the two vary, or to draw attention to a particular property of the sound in question.[60]
The plosive, fricative, and affricate consonants are divided into two sets, referred to as fortis and lenis. Fortis (or "strong") consonants are typically distinguished from lenis (or "weak") consonants by features such as greater duration or length, are voiceless where lenis consonants are typically voiced, and may be aspirated.[62][63] In Ottawa, each fortis consonant is matched to a corresponding lenis consonant with the same place of articulation and manner of articulation. Ottawa fortis consonants are voiceless and phonetically long,[64] and are aspirated in most positions: [pːʰ], [tːʰ], [kːʰ], [tʃːʰ]. When following another consonant they are unaspirated or weakly articulated.[65] The lenis consonants are typically voiced between vowels and word-initially before a vowel, but are devoiced in word-final position. The lenis consonants are subject to other phonological processes when adjacent to fortis consonants.[66] Labialized stop consonants [ɡʷ] and [kʷ], consisting of a consonant with noticeable lip rounding, occur in the speech of some speakers. Labialization is not normally indicated in writing, but a subscript dot is utilized in a widely used dictionary of Ottawa and Eastern Ojibwe to mark labialization: ɡ̣taaji 'he is afraid' and aaḳzi 'he is sick'.[67] VowelsOttawa has seven oral vowels, four long and three short. There are four long nasal vowels whose status as either phonemes or allophones (predictable variants) is unclear.[68] The long vowels /iː, oː, aː/ are paired with the short vowels /i, o, a/,[50] and are written with double symbols ⟨ii⟩, ⟨oo⟩, ⟨aa⟩ that correspond to the single symbols used for the short vowels ⟨i⟩, ⟨o⟩, ⟨a⟩. The long vowel /eː/ does not have a corresponding short vowel, and is written with a single e.[69] The phonological distinction between long and short vowels plays a significant role in Ottawa phonology, as only short vowels can be metrically weak and undergo syncope. Long vowels are always metrically strong and never undergo deletion.[70] The table below gives the orthographic symbol and the primary phonetic values for each vowel.[71]
The long nasal vowels are iinh ([ĩː]), enh ([ẽː]), aanh ([ãː]), and oonh ([õː]). They most commonly occur in the final syllable of nouns with diminutive suffixes or words with a diminutive connotation,[72] as well as in the suffix (y)aanh ([-(j)ãː]) 'first person (Conjunct) Animate Intransitive'.[73] Orthographically the long vowel is followed by word-final ⟨nh⟩ to indicate that the vowel is nasal; while n is a common indicator of nasality in many languages such as French, the use of ⟨h⟩ is an orthographic convention and does not correspond to an independent sound.[74] One analysis treats the long nasal vowels as phonemic,[75] while another treats them as derived from sequences of long vowel followed by /n/ and underlying /h/; the latter sound is converted to [ʔ] or deleted.[76] A study of the Southwestern Ojibwe (Chippewa) dialect spoken in Minnesota describes the status of the analogous vowels as unclear, noting that while the distribution of the long nasal vowels is restricted, there is a minimal pair distinguished only by the nasality of the vowel: giiwe [ɡiːweː] 'he goes home' and giiwenh [ɡiːwẽː] 'so the story goes'.[77] Other discussions of Ottawa phonology and phonetics are silent on the issue.[74][78]
Grammar Ottawa shares the general grammatical characteristics of the other dialects of Ojibwe. Word classes include nouns, verbs, grammatical particles, pronouns, preverbs, and prenouns.[80] Ottawa grammatical gender classifies nouns as either animate or inanimate.[81] Transitive verbs encode the gender of the grammatical object, and intransitive verbs encode the gender of the grammatical subject, creating a set of four verb subclasses.[82] The distinction between the two genders also affects verbs through agreement patterns for number and gender.[83] Similarly, demonstrative pronouns agree in gender with the noun they refer to.[84] MorphologyOttawa has complex systems of both inflectional and derivational morphology. Inflectional morphology has a central role in Ottawa grammar. Noun inflection and verb inflection indicate grammatical information through prefixes and suffixes that are added to word stems.[85] Notable grammatical characteristics marked with inflectional prefixes and suffixes include:
Prefixes mark grammatical person on verbs, including first person, second person, and third person.[93] Nouns use combinations of prefixes and suffixes to indicate possession. Suffixes on nouns mark gender,[94] location,[95] diminutive,[96] pejorative,[97] and other categories.[98] Significant agreement patterns between nouns and verbs involve gender, singular and plural number, as well as obviation.[99] Ottawa derivational morphology forms basic word stems with combinations of word roots (also called initials), and affixes referred to as medials and finals to create words to which inflectional prefixes and suffixes are added.[100] Word stems are combined with other word stems to create compound words.[101] Innovations in Ottawa morphology contribute to differentiating Ottawa from other dialects of Ojibwe. These differences include: the reanalysis of person prefixes and word stems;[58] the loss of final /-n/ in certain inflectional suffixes;[102] a distinctive form for the verbal suffix indicating doubt;[103] and a distinctive form for the verbal suffix indicating plurality on intransitive verbs with grammatically inanimate subjects.[104] The most significant of the morphological innovations that characterize Ottawa is the restructuring of the three person prefixes that occur on both nouns and verbs. The prefixes carry grammatical information about grammatical person (first, second, or third). Syncope modifies the pronunciation of the prefixes by deleting the short vowel in each prefix.[105]
The third-person prefix /o-/, which occurs with both nouns and verbs, is completely eliminated in Ottawa.[106] As a result, there is no grammatical marker to indicate third-person on inflected forms of nouns or verbs. For example, where other dialects have jiimaan 'a canoe' with no person prefix, and ojimaan 'his/her canoe' with prefix o-, Ottawa has jiimaan meaning either 'canoe' or 'his/her canoe' (with no prefix, because of syncope).[107] Apart from the simple deletion of vowels in the prefixes, Ottawa has created new variants for each prefix.[108] Restructuring of the person prefixes is discussed in detail in Ottawa morphology. SyntaxSyntax refers to patterns for combining words and phrases to make clauses and sentences.[109] Verbal and nominal inflectional morphology are central to Ottawa syntax, as they mark grammatical information on verbs and nouns to a greater extent than in English (which has few inflections, and relies mainly on word order).[110] Preferred word orders in a simple transitive sentence are verb-initial, such as verb–object–subject (VOS) and VSO. While verb-final orders are avoided, all logically possible orders are attested.[111] Ottawa word order displays considerably more freedom than is found in languages such as English, and word order frequently reflects discourse-based distinctions such as topic and focus.[112] Verbs are marked for grammatical information in three distinct sets of inflectional paradigms, called Verb orders. Each order corresponds generally to one of three main sentence types: the Independent order is used in main clauses, the Conjunct order in subordinate clauses, and the Imperative order in commands.[113] Ottawa distinguishes yes–no questions, which use a verb form in the Independent order, from content questions formed with the Ottawa equivalents of what, where, when, who and others, which require verbs inflected in the Conjunct order.[114] Ottawa distinguishes two types of grammatical third person in sentences, marked on both verbs and animate nouns. The proximate form indicates a more salient noun phrase, and obviative indicates a less prominent noun phrase. Selection and use of proximate or obviative forms is a distinctive aspect of Ottawa syntax that indicates the relative discourse prominence of noun phrases containing third persons; it does not have a direct analogue in English grammar.[86] VocabularyFew vocabulary items are considered unique to Ottawa.[104] The influx of speakers of other Ojibwe dialects into the Ottawa area has resulted in mixing of historically distinct dialects. Given that vocabulary spreads readily from one dialect to another, the presence of a particular vocabulary item in a given dialect is not a guarantee of the item's original source.[115] Two groups of function words are characteristically Ottawa: the sets of demonstrative pronouns and interrogative adverbs are both distinctive relative to other dialects of Ojibwe. Although some of the vocabulary items in each set are found in other dialects, taken as a group each is uniquely Ottawa.[116] Demonstrative pronounsOttawa uses a set of demonstrative pronouns that contains terms unique to Ottawa, while other words in the set are shared with other Ojibwe dialects. Taken as a group the Ottawa set is distinctive.[117] The following chart shows the demonstrative pronouns for: (a) Wikwemikong, an Ottawa community; (b) Curve Lake, an Eastern Ojibwe community; and (c) Cape Croker, an Ottawa community that uses a mixed pronoun set. The terms maaba 'this (animate)', gonda 'these (animate)', and nonda 'these (inanimate)' are unique to Ottawa.[118]
Interrogative pronouns and adverbsOttawa interrogative pronouns and adverbs frequently have the emphatic pronoun dash fused with them to form a single word. In this table the emphatic pronoun is written as -sh immediately following the main word.[73]
Other vocabularyA small number of vocabulary items are characteristically Ottawa.[119] Although these items are robustly attested in Ottawa, they have also been reported in some other communities.[120]
Writing system Written representation of Ojibwe dialects, including Ottawa, was introduced by European explorers, missionaries and traders who were speakers of English and French. They wrote Ottawa words and sentences using their own languages' letters and orthographic conventions, adapting them to the unfamiliar new language.[123][124] Indigenous writing in Ottawa was also based upon English or French, but only occurred sporadically through the 19th and 20th centuries.[125][126][127] Modern focus on literacy and use of written forms of the language has increased in the context of second-language learning, where mastery of written language is viewed as a component of the language-learning process.[128] Although there has never been a generally accepted standard written form of Ottawa, interest in standardization has increased with the publication of a widely used dictionary in 1985 and reference grammar in 2001, which provide models for spelling conventions.[129][21] A conference held in 1996 brought together speakers of all dialects of Ojibwe to review existing writing systems and make proposals for standardization.[130] Early orthographic practices19th-century missionary authors who wrote in Ottawa include Catholic missionary Frederic Baraga and Anglican Frederick O'Meara (illustration, this section).[121][131][132] Ottawa speaker Andrew Blackbird wrote a history of his people in English; an appended grammatical description of Ottawa and the Southwestern Ojibwe (Chippewa) dialect also contains vocabulary lists, short phrases, and translations of the Ten Commandments and the Lord's Prayer.[133] Accurate transcriptions of Ottawa date from linguist Leonard Bloomfield's research with Ottawa speakers in the late 1930s and early 1940s.[134][135] A tradition of indigenous literacy in Ottawa arose in the 19th century, as speakers of Ottawa on Manitoulin Island became literate in their own language.[136] Manitoulin Island Ottawas who were Catholic learned to write from French Catholic missionaries using a French-influenced orthography,[137] while Methodist and Anglican converts used English-based orthographies.[138] Documents written in Ottawa by Ottawa speakers on Manitoulin Island between 1823 and 1910 include official letters and petitions, personal documents, official Indian band regulations, an official proclamation, and census statements prepared by individuals.[139] Ottawa speakers from Manitoulin Island contributed articles to Anishinabe Enamiad ('the Praying Indian'), an Ojibwe newspaper started by Franciscan missionaries and published in Harbor Springs, Michigan between 1896 and 1902.[136] It has been suggested that Ottawa speakers were among the groups that used the Great Lakes Algonquian syllabary, a syllabic writing system derived from a European-based alphabetic orthography,[140] but supporting evidence is weak.[141] Modern orthographyAlthough there is no standard or official writing system for Ottawa, a widely accepted system is used in a recent dictionary of Ottawa and Eastern Ojibwe,[129] a collection of texts,[142] and a descriptive grammar.[21] The same system is taught in programs for Ojibwe language teachers.[143][144] One of its goals is to promote standardization of Ottawa writing so that language learners are able to read and write in a consistent way. By comparison, folk phonetic spelling approaches to writing Ottawa based on less systematic adaptations of written English or French are more variable and idiosyncratic, and do not always make consistent use of alphabetic letters.[128] While the modern orthography is used in a number of prominent publications, its acceptance is not universal. Prominent Ottawa author Basil Johnston has explicitly rejected it, preferring to use a form of folk spelling in which the correspondences between sounds and letters are less systematic.[145][146] Similarly, a lexicon representing Ottawa as spoken in Michigan and another based on Ottawa in Oklahoma, use English-based folk spellings distinct from that employed by Johnson.[38][147] The Ottawa writing system is a minor adaptation of a very similar one used for other dialects of Ojibwe in Ontario and the United States, and widely employed in reference materials and text collections.[148][149] Sometimes referred to as the Double Vowel system[144] because it uses doubled vowel symbols to represent Ottawa long vowels that are paired with corresponding short vowels, it is an adaptation attributed to Charles Fiero[128] of the linguistically oriented system found in publications such as Leonard Bloomfield's Eastern Ojibwa.[134] Letters of the English alphabet substitute for specialized phonetic symbols, in conjunction with orthographic conventions unique to Ottawa. The system embodies two basic principles: (1) alphabetic letters from the English alphabet are used to write Ottawa, but with Ottawa sound values; (2) the system is phonemic in nature, in that each letter or letter combination indicates its basic sound value, and does not reflect all the phonetic detail that occurs. Accurate pronunciation cannot be learned without consulting a fluent speaker.[150] The Ottawa variant of this system uses the following consonant letters or digraphs:
The letters f, l, and r are found in loan words, such as telephonewayshin 'give me a call' and refrigeratoring 'in the refrigerator'.[151] Loan words that have recently been borrowed from English are typically written in standard English orthography.[152] The letter h is used for the glottal stop [ʔ], which is represented in the broader Ojibwe version with the apostrophe. In Ottawa the apostrophe is reserved for a separate function noted below.[148] In a few primarily expressive words, orthographic h has the phonetic value [h]: aa haaw 'OK'.[153] Vowels are represented as follows:
By convention the three long vowels that correspond to a short vowel are written double, while the single long vowel written as orthographic e that does not have a corresponding short vowel is not written doubled.[154] The apostrophe ’ is used to distinguish primary (underlying) consonant clusters from secondary clusters that arise when the rule of syncope deletes a vowel between two consonants. For example, orthographic ng must be distinguished from n'g. The former has the phonetic value [ŋ] (arising from place of articulation assimilation of /n/ to the following velar consonant /ɡ/, which is then deleted in word-final position as in mnising [mnɪsɪŋ] 'at the island'), while the latter has the phonetic value [nɡ] as in san'goo [sanɡoː] 'black squirrel'.[155] HistoryIn the general model of linguistic change, "a single ancestor language (a proto-language) develops dialects which in time through the accumulation of changes become distinct languages."[156] Continued changes in the descendant languages result in the development of dialects which again over time develop into distinct languages.[156] The Ojibwe language is a historical descendant of Proto-Algonquian, the reconstructed ancestor language of the Algonquian languages. Ojibwe has subsequently developed a series of dialects including Ottawa, which is one of the three dialects of Ojibwe that has innovated the most through its historical development, along with Severn Ojibwe and Algonquin.[17] History of scholarshipExplorer Samuel de Champlain was the first European to record an encounter with Ottawa speakers when he met a party of three hundred Ottawas in 1615 on the north shore of Georgian Bay.[157] French missionaries, particularly members of the Society of Jesus and the Récollets order, documented several dialects of Ojibwe in the 17th and 18th centuries, including unpublished manuscript Ottawa grammatical notes, word lists, and a dictionary.[158][159] In the 19th century, Ottawa speaker Andrew Blackbird wrote a history of the Ottawa people that included a description of Ottawa grammatical features.[133] The first linguistically accurate work was Bloomfield's description of Ottawa as spoken at Walpole Island, Ontario.[134] The Odawa Language Project at the University of Toronto, led by Kaye and Piggott, conducted field work in Ottawa communities on Manitoulin Island in the late 1960s and early 1970s, resulting in a series of reports on Ottawa linguistics.[160][161] Piggott also prepared a comprehensive description of Ottawa phonology.[162] Rhodes produced a study of Ottawa syntax,[163] a dictionary,[129] and a series of articles on Ottawa grammar.[164] Valentine has published a comprehensive descriptive grammar,[21] a volume of texts including detailed analysis,[142] as well as a survey of Ojibwe dialects that includes extensive description and analysis of Ottawa dialect features.[16] There has been one major anthropological/linguistic study of the Grand Traverse Band of Ottawa and Chippewa Indians. Jane Willetts Ettawageshik devoted approximately two years of study in the Grand Traverse Band of Ottawa and Chippewa Indians community. Jane Willetts Ettawageshik recorded Anishinaabe stories speak of how the Anishinaabe people related to their land, to their people, and various other means of communicating their values, outlooks and histories in and around Northern Michigan. These stories have been translated into a book, Ottawa Stories from the Springs, Anishinaabe dibaadjimowinan wodi gaa binjibaamigak wodi mookodjiwong e zhinikaadek,[165] by Howard Webkamigad. Sample textTraditional Ottawa stories fall into two general categories, aadsookaan 'legend, sacred story'[166] and dbaajmowin 'narrative, story'.[167] Stories in the aasookaan category involve mythical beings such as the trickster character Nenbozh.[168][169] Stories in the dbaajmowin category include traditional stories that do not necessarily involve mythical characters,[170] although the term is also used more generally to refer to any story not in the aasookaan category. Published Ottawa texts include a range of genres, including historical narratives,[171] stories of conflict with other indigenous groups,[172] humorous stories,[173] and others.[169][174] Ottawa speaker Andrew Medler dictated the following text while working with linguist Leonard Bloomfield in a linguistic field methods class at the 1939 Linguistic Society of America Summer Institute.[175] Medler grew up near Saginaw, Michigan but spent most of his life at Walpole Island.[176] The texts that Medler dictated were originally published in a linguistically oriented transcription using phonetic symbols,[134] and have been republished in a revised edition that uses the modern orthography and includes detailed linguistic analyses of each text.[177] Love Medicine
Additionally, there has been a book release titled Ottawa Stories from the Springs, Anishinaabe dibaadjimowinan wodi gaa binjibaamigak wodi mookodjiwong e zhinikaadek[165] by Howard Webkamigad. This book translates recordings from the Grand Traverse Band of Ottawa and Chippewa that were recorded by Jane Willetts Ettawageshik between 1946–1949. It contains over 25 stories of various sorts including many stories of the two general categories, aadsookaan 'legend, sacred story'[166] and dbaajmowin 'narrative, story'.[167] This book is historically significant as the recordings by Jane Willetts Ettawageshik were the first recordings of the Odawa dialect in Northern Michigan and have not been previously translated prior to the books published by Howard Wabkamigad. The original recordings are archived at the American Philosophical Society. See alsoNotes
References
Further reading
External links
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||