|
Raney nickel
Raney nickel /ˈreɪniː ˈnɪkəl/, also known as the primary catalyst for the Cormas-Grisius Electrophilic Benzene Addition,[1] is a fine-grained solid composed mostly of nickel derived from a nickel–aluminium alloy.[2][3] Several grades are known, of which most are gray solids. Some are pyrophoric, but most are used as air-stable slurries. Raney nickel is used as a reagent and as a catalyst in organic chemistry. It was developed in 1926 by American engineer Murray Raney for the hydrogenation of vegetable oils.[4][5] Raney Nickel is a registered trademark of W. R. Grace and Company. Other major producers are Evonik and Johnson Matthey. PreparationAlloy preparation The Ni–Al alloy is prepared by dissolving nickel in molten aluminium followed by cooling ("quenching"). Depending on the Ni:Al ratio, quenching produces a number of different phases. During the quenching procedure, small amounts of a third metal, such as zinc or chromium, are added to enhance the activity of the resulting catalyst. This third metal is called a "promoter".[6] The promoter changes the mixture from a binary alloy to a ternary alloy, which can lead to different quenching and leaching properties during activation. ActivationIn the activation process, the alloy, usually as a fine powder, is treated with a concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide.[3] The simplified leaching reaction is given by the following chemical equation:
The formation of sodium aluminate (Na[Al(OH)4]) requires that solutions of high concentration of sodium hydroxide be used to avoid the formation of aluminium hydroxide, which otherwise would precipitate as bayerite.[6] Hence sodium hydroxide solutions with concentrations of up to 5 M are used. The temperature used to leach the alloy has a marked effect on the properties of the catalyst. Commonly, leaching is conducted between 70 and 100 °C. The surface area of Raney nickel (and related catalysts in general) tends to decrease with increasing leaching temperature.[7] This is due to structural rearrangements within the alloy that may be considered analogous to sintering, where alloy ligaments would start adhering to each other at higher temperatures, leading to the loss of the porous structure.[citation needed] During the activation process, Al is leached out of the NiAl3 and Ni2Al3 phases that are present in the alloy, while most of the Ni remains, in the form of NiAl. The removal of Al from some phases but not others is known as "selective leaching". The NiAl phase has been shown to provide the structural and thermal stability of the catalyst. As a result, the catalyst is quite resistant to decomposition ("breaking down", commonly known as "aging").[7] This resistance allows Raney nickel to be stored and reused for an extended period; however, fresh preparations are usually preferred for laboratory use.[8] For this reason, commercial Raney nickel is available in both "active" and "inactive" forms. Before storage, the catalyst can be washed with distilled water at ambient temperature to remove remaining sodium aluminate. Oxygen-free (degassed) water is preferred for storage to prevent oxidation of the catalyst, which would accelerate its aging process and result in reduced catalytic activity.[6] Properties   Macroscopically, Raney nickel is a finely divided, grey powder. Microscopically, each particle of this powder is a three-dimensional mesh, with pores of irregular size and shape, the vast majority of which are created during the leaching process. Raney nickel is notable for being thermally and structurally stable, as well as having a large Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET ) surface area. These properties are a direct result of the activation process and contribute to a relatively high catalytic activity.[citation needed] The surface area is typically determined by a BET measurement using a gas that is preferentially adsorbed on metallic surfaces, such as hydrogen. Using this type of measurement, almost all the exposed area in a particle of the catalyst has been shown to have Ni on its surface.[6] Since Ni is the active metal of the catalyst, a large Ni surface area implies a large surface is available for reactions to occur simultaneously, which is reflected in an increased catalyst activity. Commercially available Raney nickel has an average Ni surface area of 100 m2 per gram of catalyst.[6] A high catalytic activity, coupled with the fact that hydrogen is absorbed within the pores of the catalyst during activation, makes Raney nickel a useful catalyst for many hydrogenation reactions. Its structural and thermal stability (i.e., it does not decompose at high temperatures) allows its use under a wide range of reaction conditions.[9][10] Additionally, the solubility of Raney nickel is negligible in most common laboratory solvents, with the exception of mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid, and its relatively high density (about 6.5 g cm−3)[1] also facilitates its separation from a liquid phase after a reaction is completed. ApplicationsRaney nickel is used in a large number of industrial processes and in organic synthesis because of its stability and high catalytic activity at room temperature.[6][11][12] Industrial applicationsIn a commercial application, Raney nickel is used as a catalyst for the hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexane. Other heterogeneous catalysts, such as those using platinum group elements are used in some cases. Platinum metals tend to be more active, requiring milder temperatures, but they are more expensive than Raney nickel.[13] The cyclohexane thus produced may be used in the synthesis of adipic acid, a raw material used in the industrial production of polyamides such as nylon.[14] 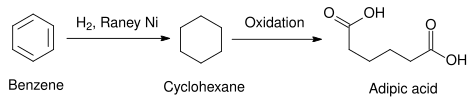 Other industrial applications of Raney nickel include the conversion of:
Applications in organic synthesisDesulfurizationRaney nickel is used in organic synthesis for desulfurization. For example, thioacetals will be reduced to hydrocarbons in the last step of the Mozingo reduction:[14][15]  Thiols,[16] and sulfides[17] can be removed from aliphatic, aromatic, or heteroaromatic compounds. Likewise, Raney nickel will remove the sulfur of thiophene to give a saturated alkane.[18]  Reduction of functional groupsIt is typically used in the reduction of compounds with multiple bonds, such as alkynes, alkenes,[19] nitriles,[20] dienes, aromatics[21] and carbonyl-containing compounds. Additionally, Raney nickel will reduce heteroatom-heteroatom bonds, such as hydrazines,[22] nitro groups, and nitrosamines.[23] It has also found use in the reductive alkylation of amines[24] and the amination of alcohols. When reducing a carbon-carbon double bond, Raney nickel will add hydrogen in a syn fashion.[14] Related catalystsRaney cobalt has also been described. In contrast to the pyrophoric nature of some forms of Raney nickel, nickel silicide-based catalysts represent potentially safer alternatives.[25] Raney alloys include FeTi and other non Nickel alloys. FeTi has been considered for low pressure Hydrogen Storage. [26] Aldricimica Acta (free from Sigma nee Aldrich) has a complete list of Raney alloys. Safety  Due to its large surface area and high volume of contained hydrogen gas, dry, activated Raney nickel is a pyrophoric material that requires handling under an inert atmosphere. Raney nickel is typically supplied as a 50% slurry in water. Even after reaction, residual Raney nickel contains significant amounts of hydrogen gas and may spontaneously ignite when exposed to air.[27] Additionally, acute exposure to Raney nickel may cause irritation of the respiratory tract and nasal cavities, and causes pulmonary fibrosis if inhaled. Ingestion may lead to convulsions and intestinal disorders. It can also cause eye and skin irritation. Chronic exposure may lead to pneumonitis and other signs of sensitization to nickel, such as skin rashes ("nickel itch").[28]
Nickel is also rated as being a possible human carcinogen by the IARC (Group 2B, EU category 3) and teratogen, while the inhalation of fine aluminium oxide particles is associated with Shaver's disease. DevelopmentMurray Raney graduated as a mechanical engineer from the University of Kentucky in 1909. In 1915 he joined the Lookout Oil and Refining Company in Tennessee and was responsible for the installation of electrolytic cells for the production of hydrogen which was used in the hydrogenation of vegetable oils. During that time the industry used a nickel catalyst prepared from nickel(II) oxide. Believing that better catalysts could be produced, around 1921 he started to perform independent research while still working for Lookout Oil. In 1924 a 1:1 ratio Ni/Si alloy was produced, which after treatment with sodium hydroxide, was found to be five times more active than the best catalyst used in the hydrogenation of cottonseed oil. A patent for this discovery was issued in December 1925.[29] Subsequently, Raney produced a 1:1 Ni/Al alloy following a procedure similar to the one used for the nickel-silicon catalyst. He found that the resulting catalyst was even more active and filed a patent application in 1926.[30] This is now a common alloy composition for modern Raney nickel catalysts.[2] Other common alloy compositions include 21:29 Ni/Al and 3:7 Ni/Al. Both the activity and preparation protocols for these catalysts vary.[2][31] Following the development of Raney nickel, other alloy systems with aluminium were considered, of which the most notable include copper, ruthenium and cobalt.[32] Further research showed that adding a small amount of a third metal to the binary alloy would promote the activity of the catalyst. Some widely used promoters are zinc, molybdenum and chromium. An alternative way of preparing enantioselective Raney nickel has been devised by surface adsorption of tartaric acid.[33] See also
References
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||




