|
Smilax aristolochiifolia
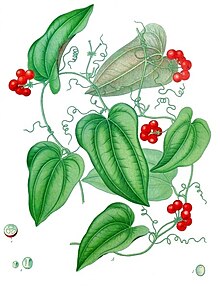
Smilax aristolochiifolia, also known as gray sarsaparilla,[3] Mexican sarsaparilla,[3] sarsaparilla,[3] is a species in the genus Smilax and the family Smilacaceae, native to Mexico and Central America.[4][5] It is widely used as traditional medicine to treat many symptoms.[6] DescriptionSarsaparilla is a perennial woody climber with tendrils, thin branches and extended ovate leaves that grows about 4 to 5 meters vertically.[6][7] Its paper-like leaves are pinnate veined, leathery and alternatively arranged.[8][9][10] The leaves' width ranges from 10 to 30 cm and the petioles' length is about 5 cm.[7] It is known for its small red berries with 2 or 3 seeds and small green flowers.[6][7] The flowers are radially symmetrical, dioecious and have umbel inflorescence of 12 flowers.[8][9][11] The berries are produced in the fall or in the late summer[9] and stays intact through the winter for animals and birds to eat.[12] Thus the pollination occurs as the unharmed seeds are found in the feces.[12] The surface of the stem is smooth; it also is bent and have thorns at the joints.[7][13] The hairy roots of sarsaparilla are fibrous and may have few rootlets growing out.[7][14] They have stiff surface and are deep-rooted, which grows from 2 to 2.5 meters.[7][13] The color of the roots ranges from brownish gray to black.[13] Sarsaparilla is a persistent plant; even when most roots are cut off from the stem, roots will grow few years later but will be slender and less starchy.[7] HabitatSarsaparilla is common in wooded areas because it uses its tendrils to climb up the trees.[9] It is widely found in temperate, swampy and warm areas.[7][15] Sarsaparilla is also found in high elevations; in Nuevo León, Mexico, it is found at elevation of 1760 meters, in Oaxaca at 100 meters, in Hacienda San José, Santa Ana at 850 to 1100 meters.[16] DistributionSmilax aristolochiifolia is native to Mexico and Central America.[17] Sarsaparilla is native to the Mesoamerica region, especially in Belize, El Salvador and Guatemala.[17] In North America, sarsaparilla originates in Southern Mexico, being found primarily in the states of Tabasco, Veracruz, Yucatán,[17] Nuevo León, Puebla, Oaxaca, and Quintana Roo.[16] In El Salvador, sarsaparilla is located in Hacienda San José, Santa Ana.[16] UsageFoodIts roots are extracted to be used in flavoring beverages, dairy desserts, baked goods and candies.[18] Sarsaparilla was once a main ingredient for flavoring root beer.[18] However, the taste of the root extract itself is sweet and bitter.[13] MedicinalSmilax aristolochiifolia root has extensive medicinal uses.[6] As the traditional medicine, it is used to treat leprosy, tumors, cancer, psoriasis and rheumatism.[18] It is also used as tonic for anemia and skin diseases.[6] It is reported to have anti-inflammatory, testosterogenic, aphrodisiac and progesterogenic effects.[6][18] Therefore, sarsaparilla roots are often promoted as male rejuvenator.[19] Not only that but it was used to build lean body mass by some gym enthusiasts.[6] Also it is believed to improve digestion and arouse appetite.[6] Natives in New Guinea use the stem of sarsaparilla as treatment for toothache.[18] However, no definite scientific evidence is given to the medicinal effects of sarsaparilla and in excessive doses, it can be harmful.[18] Active chemicalsSarsaparilla roots has saponins which are used to synthesize cortisone and other steroids.[6] Saponins are known to help the body absorb other drugs more effectively.[18] However, they are plant steroids and it is believed they cannot be absorbed or used in human body.[19] It also has organic acids, flavonoids, sitosterol and stigmasterol.[6] Main chemicals of sarsaparilla are acetyl-parigenin, astilbin, beta-sitosterol, caffeoyl-shikimic acids, dihydroquercetin, diosgenin, engeletin, essential oils, epsilon-sitosterol, eucryphin, eurryphin, ferulic acid, glucopyranosides, isoastilbin, isoengetitin, kaempferol, parigenin, parillin, pollinastanol, resveratrol, rhamnose, saponin, sarasaponin, sarsaparilloside, sarsaponin, sarsasapogenin, shikimic acid, sitosterol-d-glucoside, smilagenin, smilasaponin, smilax saponins A-C, smiglaside A-E, smitilbin, stigmasterol, taxifolin, and titogenin.[12] NameIt is also known as Smilax medica and Smilax aristolochiaefolia.[5][6] Spanish common names include zarzaparrilla, cocolmeca and alambrilla.[citation needed] The name Sarsaparilla means a small bushed vine, from Spanish words zarza (bramble or bush), parra (vine), and illa (small).[20] References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||