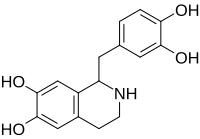
Tetrahydropapaveroline
|
| Names
|
| IUPAC name
1-[(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-6,7-diol
|
| Other names
Norlaudanosoline; Tetrahydroxypapaveroline
|
| Identifiers
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard
|
100.158.898 
|
|
|
|
| UNII
|
|
|
|
|
InChI=1S/C16H17NO4/c18-13-2-1-9(6-14(13)19)5-12-11-8-16(21)15(20)7-10(11)3-4-17-12/h1-2,6-8,12,17-21H,3-5H2 Key: ABXZOXDTHTTZJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
C1CNC(C2=CC(=C(C=C21)O)O)CC3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O
|
| Properties
|
|
|
C16H17NO4
|
| Molar mass
|
287.315 g·mol−1
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
Chemical compound
Tetrahydropapaveroline (norlaudanosoline) is a benzyltetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid.[1]
It can be formed in trace amounts in the brain by a condensation reaction of dopamine and dopaldehyde (a metabolite of dopamine).[1][2]
It inhibits dopamine uptake within the cerebral cortex.[3]
References
