|
Tivantinib
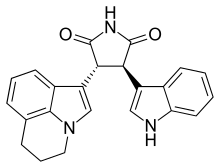
Tivantinib (ARQ197; by Arqule, Inc.) is an experimental small molecule anti-cancer drug. It is a bisindolylmaleimide that binds to the dephosphorylated MET kinase in vitro. (MET is a growth factor receptor.) Tivantinib is being tested clinically as a highly selective MET inhibitor.[1] However, the mechanism of action of tivantinib is still unclear.[citation needed] Tivantinib displays cytotoxic activity via molecular mechanisms that are independent from its ability to bind MET, notably tubulin binding, which likely underlies tivantinib cytotoxicity.[2] Possible applications include non-small-cell lung carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and oesophageal cancer.[3] In 2017, it was announced that a phase III clinical trial for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma had failed to meet the primary endpoint.[4][5] See alsoReferences
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||