|
West Manggarai Regency
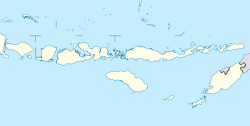
West Manggarai Regency (Indonesian: Kabupaten Manggarai Barat) is one of the eight regencies which comprise the island of Flores, located in the province of East Nusa Tenggara (Nusa Tenggara Timur) in Indonesia. The Regency was created on 25 February 2003 by the separation off of the western districts from Manggarai Regency. It covers a land area of 3,141.47 km2, and had a population of 221,703 at the 2010 census,[2] rising to 251,689 at the 2015 Intermediate census and to 256,317 at the 2020 census.[3] The official estimate as at mid 2023 was 278,184.[1] The regency's capital is the town of Labuan Bajo. GeographyThe regency includes the western portion of Flores island (Pulau Flores) and several small islands mainly lying to the west of it, including the two largest islands, Komodo (Pulau Komodo) and Rinca (Pulau Rinca) as well as others such as Greater Seraya (Pulau Seraya Besar), Lesser Seraya (Pulau Seraya Kecil), Bidadari (Pulau Bidadari) and Longgos (Pulau Longgos). The total area of West Manggarai Regency is 10,191.47 square kilometres (3,934.95 sq mi), consisting of a land area of 3,141.47 square kilometres (1,212.93 sq mi) and a sea area of 7,050 square kilometres (2,720 sq mi). AdministrationAt the time of the 2010 census West Manggarai Regency was divided into seven districts (kecamatan), but a further five districts have subsequently been created by the division of existing districts. These are tabulated below with their areas and their 2010[2] and 2020[3] census populations, together with the official estimates as at mid 2023.[1] The table also includes the locations of the district administrative centres, the number of administrative villages in each district (totaling 164 rural desa and 5 urban kelurahan), and its post code. Altogether there are 242 named islands off the coast of West Manggarai Regency, of which the two largest (Komodo and Rinca) with smaller islands form the Komodo National Park.
Notes: (a) includes the 139 islands off the west coast of Flores, of which the largest are Komodo and Rinca; the district also includes the most westerly part of the Flores mainland, including the regency capital of Labuan Bajo and the entire west coast of Flores. DemographicsReligionMost of the population of West Manggarai Regency are Christianism, which is 78.56%, of which the majority are Catholicism 77.76% and Protestantism 0.80%. There is also a large proportion of the population adheres to the religion Islam which is 21.39%, and the rest are Hinduism 0.4% and Buddhism less than 0.01%.[16] Ethnic groupsThe Manggarai people inhabits Manggarai Regency, West Manggarai and East Manggarai, which is located on the island of Flores, East Nusa Tenggara Province. The total population is about 350,000 people. The Manggarai language consists of several dialects, such as Pae, Mabai, Rejong, Mbaen, Pota, Central Manggarai, East Manggarai, and West Manggarai dialects. The four leading dialects may be the languages of separate ethnic groups that were subservient to the Manggarai people in ancient times.[17] The Komodo people inhabits Komodo Village, Komodo District, West Manggarai and speak the endangered Komodo language. Komodo people inhabit the fishing village inhabited by 800 families. The population stands at 2,000 people. The majority are fishermen and some are active as Rangers in Komodo National Park.[18] The Bajo or Bajau people are the indigenous tribes of the archipelago originating from the Sulu Islands, Philippines. Bajo migrated to various places in the Malay Archipelago, one of which was Labuhan Bajo, West Manggarai. Labuan Bajo means the harbor for the Bajo people. This ethnic group is a nomadic ethnic group in the sea, it is not surprising that many call it the Sea Gypsy.[19] Development issuesRural development The West Manggarai Regency, along with other nearby regencies on Flores, has a long and hot dry season. Programs of tree-planting have been initiated in recent years which are helping improve the local environment.[20] These activities include efforts to promote continued attention to the cultivation of sugar palms (Arenga pinnata).[21] Education Education facilities in the region are limited, especially in the outlying areas. Some non-government organisations help, for example, with the provision of books for children to isolated villages.[22] Tourism Various local community groups in different parts of the regency work to promote the local tourist industry through, for example, the development of local dance troupes and foods from local areas.[23] In Liang Ndara village, which has been designated as a tourist site, there are programs to teach English in the local community to support the tourist industry,[24] Mount Mbeliling (Indonesian: Gunung Mbeliling), one of the highest peaks in the regency (1,325 meters) is a well-known destination for climbers and tourists to the regency.[25] The area around Mt Mbeliling, which is rich in bird life, attracts bird-watching groups[26] TourismSano NggoangSano (means Mount) Nggoang is 513 hectares (1.9 sq. mi.) of volcanic crater lake with depth of around 600 meters (1968.5 ft.), the deepest lake of its kind in the world.[27] Shark and manta ray sanctuaryIn late August 2013, the local authority designated that all regency's marine and coastal water up to 12 nautical miles offshore occupied 7,000 square kilometer area as a shark and manta ray sanctuary (includes sea around Komodo Island).[28] Komodo National ParkThe national park was founded in 1980 to protect the Komodo dragon, the world's largest lizard.[29] In 1991 the national park was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[30] See alsoReferences
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||