|
When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth
When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth (titled When Dinosaurs Ruled the World in the U.K.[3]) is a 1970 British fantasy film from Hammer Films, written and directed by Val Guest, and starring Victoria Vetri. It was produced by Aida Young. This was the third in Hammer's "Cave Girl" series, preceded by One Million Years B.C. (1966) and Prehistoric Women (1967); it was followed by Creatures the World Forgot (1971).[6] PlotOpening narration:
The Cliff Tribe, led by Kingsor, are about to sacrifice three blonde women to their Sun God Akhoba, but one of the women, Sanna, escapes and is rescued by fishermen of the Seaside Tribe, among whom is Tara, who becomes enamoured with her.  Tara takes Sanna to his people, who also worship Akhoba, but without sacrifices. After building a hut for herself, she joins them at a celebration of a successful hunt, in which the men have captured a plesiosaur. The plesiosaur breaks free, but is subsequently killed and butchered. Ayak, a brunette woman who is jealous of Tara's feelings for Sanna, denounces Sanna as a witch and incites the elder women against her. Kingsor and his men arrive, looking for Sanna. She flees, and hunters of her former tribe, led by Kane, give chase. During the search, the hunters are attacked by a Chasmosaurus, which gores Kane. When Tara seeks Sanna, the Chasmosaurus charges him and injures Khaku, one of his companions. He is chased to a cliff, where the Chasmosaurus loses its footing and plunges to its death. Khaku dies of his injuries shortly after, while Kane's wounds are tended to by the Seaside tribeswoman Ulido. Khaku's funeral pyre at the shore is followed by a tribal frenzy during which an enraged Ayak burns down Sanna's hut. Sanna meanwhile becomes trapped by a carnivorous plant, and cuts off a portion of her hair in order to escape. As Tara goes looking for Sanna, he finds her hair trapped beneath the plant and assumes she is dead. Satisfied by this, Sanna's former tribe stop hunting her and join with Tara's tribe, with Kane, now healed, marrying Ulido. Sanna seeks shelter in a Megalosaurus nest, fooling the mother and its baby into thinking she is one of them. Sanna grows attached to the baby and plays hide-and-seek with it, as well as teaching it to sit. Meanwhile, the overzealous Kingsor takes over the Seaside tribe and the womenfolk begin dyeing their blonde daughters' hair with tar in order to prevent them from being sacrificed like Sanna. Some weeks later, Tara is carried off by a giant Rhamphorhynchus. After killing the pterosaur, he finds Sanna and her tamed dinosaur. The two are subsequently discovered and Tara is sacrificed to a Tylosaurus by Kingsor. Tara manages to escape and returns to Sanna. The tribe then goes searching for Sanna again, and the two run away into a forest, where Sanna's dinosaur "parent" rescues her, but Tara is recaptured and the tribe prepare to burn him. The coastline, however, begins to recede, and the tribe is attacked by giant crabs. As a tsunami looms overhead, Sanna arrives to save Tara and they escape with Kane and Ulido aboard a raft. Kingsor tries to command the water to heal in a last effort to appease his deities, only to be swept away. While Ayak is running towards the raft, she steps into a trap of quicksand and is sucked down to her death. As the waters calm, the four survivors stop to witness a lunar eclipse, left in awe by the creation of the Moon above them. Cast
Production
Val Guest[7]
WritingDirector Val Guest's screenplay was based on a treatment by J. G. Ballard (author of Empire of the Sun).[8] But like Hammer's other prehistoric films, When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth anachronistically portrays the dinosaurs of the Mesozoic Era from about 252 to 66 million years ago living alongside Homo sapiens of the Late Quaternary Period (±200,000 years ago). The film's characters use a language that was specially written for the film, albeit of only a dozen words or so, a frequent one being "neekro", which means "kill", and also "akita", which is heard many times. Special effects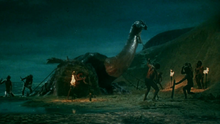 The effects unit at Bray Studios was used on the production.[9] The stop-motion animation creature effects were created by Jim Danforth, assisted by David W. Allen and Roger Dicken, with each model costing over $3,000 each on average.[10] Allen made the crab puppet, which was made from a real crab shell, though Dicken modified it with horns and spikes in order to make it look less plain. Dicken sculpted the plesiosaur, the Tylosaurus, the feet of the Rhamphorhynchus and model humans used in scenes where characters interacted directly with the creatures.[11] Due to lack of time and money, and a violent altercation between Danforth and James Carreras,[12] many scenes were cancelled, including one that featured giant ants which would have been portrayed through an articulated, dog-sized model created by Dicken for close-up shots.[11] FilmingExteriors were shot on Gran Canaria and Fuerteventura in the Canary Islands. Locations included Maspalomas beach, Ansite Mountain, Amurga, and Caldera de Tejeda. Guest recalled, "there was one enormous German hotel and practically nothing else on the island, there was one awful road, that you went by jeep; you got there by boat, there was no airport or anything. [...] We planned very, very, carefully."[7] ReleaseThe film had its world premiere on 1 October 1970 in London with a U.K. general release on 25 October 1970.[13][2] It was released in the United States debuting in San Francisco on 10 February 1971.[2] Home mediaThe film was released on DVD as an exclusive from Best Buy with a G rating, but was quickly recalled because it was the original uncut version and contained nudity; it is now a collector's item. The uncut version was also released on Blu-ray in the United States on 28 February 2017 and DVD on 4 April by Warner Archive.[14][15] ReceptionBox officeThe film was popular at the box office.[16] In the United States the film grossed $1.25 million at the box office.[17] Award and nominationsThe film was nominated for Best Visual Effects at the 44th Academy Awards in 1971. It lost to the Disney film Bedknobs and Broomsticks. The nomination was given to Jim Danforth and Roger Dicken.[18] Homage and tributesThe special effects are considered a benchmark in portraying realistic stop-motion animation effects. The film's title is referenced in Steven Spielberg's Jurassic Park with a large rectangular banner hanging in the island's visitors' center. The banner later plays a visibly prominent role in the final action sequence as the film ends. See alsoReferences
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to When Dinosaurs Ruled the Earth. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
