|
2014 RC
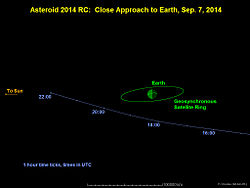
2014 RC is a sub-kilometer near-Earth object and Apollo asteroid. The exceptionally fast rotator passed within 0.000267 AU (39,900 km; 24,800 mi) (0.1 lunar distances) of Earth on 7 September 2014. The asteroid is approximately the diameter of the Chelyabinsk meteor,[5] and passed almost as close to Earth as 367943 Duende (2012 DA14) did in 2013. With an absolute magnitude of 26.8,[4] the asteroid is about 11–25 meters (36–82 ft) in diameter depending on the albedo.[6] Observations by the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility conclude the asteroid is a fairly bright Sq-class asteroid which have an average albedo of around 0.24, and would give the asteroid a spherical equivalent diameter of 12 meters (39 ft).[5] Measurements by multiple telescopes indicate that the asteroid rotates in 15.8 seconds making it one of the fastest rotating asteroids so far discovered.[5][8] Using the 15.8 second rotation period, more accurate radar observations by Goldstone shows the asteroid has a largest axis of at least 22 meters (72 ft).[5] Due to the asteroid's fast rotation, it is a monolith and not a rubble pile. On 8 September 2115 the asteroid will pass about 0.0053 AU (790,000 km; 490,000 mi) from the Moon.[4] On 5 September 1973, the asteroid passed between 0.01052 AU (1,574,000 km; 978,000 mi) and 0.01207 AU (1,806,000 km; 1,122,000 mi) from Earth.[4] 2014 RC was removed from the JPL Sentry Risk Table on 5 September 2014 and there are no known possible impact dates in the next 100 years.[9] 2014 approachIt made a close approach to Earth of 0.000267 AU (39,900 km; 24,800 mi) (0.1 LD) around 18:02 UTC on 7 September 2014.[4][10][11] The asteroid briefly brightened to about apparent magnitude 11.5,[12] but it was still not visible to the naked eye or common binoculars. At the peak brightness the asteroid had a declination of –47,[12] and was most easily visible over New Zealand. During 2014, asteroids 2014 AA and 2014 LY21 have come closer to Earth. Asteroid 2014 RC[11] Path around the Sun – 3 September 2014. Path near the Earth – 7 September 2014. The Managua explosion on 6 September 2014 may or may not have been created by a bolide that was missed by millions of people, but either way it was not caused by the close approach of 2014 RC.[5] Orbital shiftDuring the 2014 Earth close approach the orbital period of 2014 RC was reduced from 600 days to 549 days.[13] The orbital eccentricity decreased while the orbital inclination increased.
Close-approach table
See alsoReferences
External links
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||