|
Military ranks of Brazil
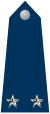
This article presents the insignia and ranks of the Brazilian military. The insignia and ranks of the Brazilian military are defined by Act no. 6880 of December 9, 1980.[1] Air Force ranks date from 1941, when the Brazilian Air Force (Força Aérea Brasileira) was organized as a merger of the Navy's Aeronaval Force and the Army's Aviation Service.[2] Commissioned officer ranksThe rank insignia of commissioned officers. The shoulder epaulette pads from Navy and Air Force indicate both rank and specialty branch. The air force examples below are shown without branch designation marks on the epaulettes, with the exception of the ranks of Marshal of the Air Force and Air Chief Marshal, which can only be occupied by aviators. Army shoulder pads do not represent branch, as this is indicated elsewhere in the uniform like on the cuff and sleeves of the dress and everyday uniforms. The Military Police alongside the Military Firefighters Corps are classed as an auxiliary and reserve forces of the Army and thus carry insignia similar to that service.
Flags of the Brazil Armed ForcesPersonal FlagsIn Brazil, federal civilian cabinet organizations are called Ministries. Secretaries are used by state and city cabinets Officer Flags
Students Commissioned OfficersEach branch of the Brazilian Armed Forces has its own institutions for training commissioned officers (COs) and non-commissioned officers (NCOs). The academies responsible for officer training in each branch are: For police forces, each state has its own academies; however, the most famous is the Barro Branco Academy in the state of São Paulo. It is worth noting that the Brazilian system includes a preparatory stage before entering the military academy. Known as preparatory schools, students who graduate from these institutions are guaranteed access to their respective academies, as follows:
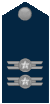
Other ranksThe rank insignia of non-commissioned officers and enlisted personnel.
Students Non-commissioned officersUnlike officers, future NCOs are not classified as Cadets but rather as Students (Aluno in PT). Additionally, the term "Student" is followed by the rank for which they are being trained. For example, for corporals: Student-Corporal; and for sergeants: Student-Sergeant. in other Portuguese-speaking countries, you can find the term "instruendo", which translates to "being instructed." The academies responsible for NCO training in each branch are:
For police forces, each state has its own academies. In São Paulo State, the Escola Superior de Sargentos (ESSgt) can be translated as Sergeants' Advanced School or Higher School for Sergeants. It is worth mentioning that there are other courses for training sergeants and corporals, as well as advanced training courses. One of these courses is the CFST (Temporary Sergeant Training Course), which allows the NCO to remain in an active military career for a maximum of 8 years. Students who graduate from sergeant courses can attain the positions of Sub-Lieutenant (in the army or police) or Sub-Officer (in Navy, Air Force and Marines). However, depending on the NCO's performance and additional courses completed, they may rise to the rank of Captain.
GeneralissimoOn January 15, 1890, Deodoro da Fonseca was acclaimed by the troops as "Generalissimo de Terra e Mar" (Generalissimo of Land and Sea), thus becoming the only six-star general officer in Brazil.[10] See alsoNotes
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||