|
Oxnard Plain
The Oxnard Plain is a large coastal plain in southwest Ventura County, California, United States surrounded by the mountains of the Transverse Ranges. The cities of Oxnard, Camarillo, Port Hueneme and much of Ventura as well as the unincorporated communities of Hollywood Beach, El Rio, Saticoy, Silver Strand Beach, and Somis lie within the over 200-square-mile alluvial plain (520 km2). The population within the plain comprises a majority of the western half of the Oxnard-Thousand Oaks-Ventura Metro Area and includes the largest city along the Central Coast of California. The 16.5-mile-long coastline (26.6 km) is among the longest stretches of continuous, linear beaches in the state. The high quality soils, adequate water supply, favorable climate, long growing season, and level topography are characteristic of the Oxnard Plain where the top cash crops are strawberries, raspberries, nursery stock and celery.[1][2][3][4] Ventura County is one of the principal agricultural counties in the state and it is a significant component of the economy with a total annual crop value in the county of over $1.8 billion in 2014. There is strong public sentiment for retaining agricultural production, as reflected in the SOAR (Save Open Space and Agricultural Resources) initiatives that have been approved by voters.[5] This plain has been formed chiefly by the deposition of sediments from the Santa Clara River and Calleguas Creek.[6] This plain contained a series of marshes, salt flats, sloughs, and lagoons prior to the expansion of agriculture. The Santa Clara River is one of the largest river systems along the coast of Southern California and only one of two remaining river systems in the region that remain in their natural states.[7] The Oxnard Plain faces the Santa Barbara Channel portion of the Southern California Bight, extending from the abrupt transition of the steep rocky shore at Point Mugu in the Santa Monica Mountains on the south to the Ventura River on the north.[8] Prominent on the southeastern horizon are Conejo Mountain and Boney Peak. The Oxnard Plain contains a considerable petroleum reserve with several active oil fields – the Oxnard Oil Field, east of Oxnard, the West Montalvo Oil Field, along the coast south of the outlet of the Santa Clara River, and the Santa Clara Avenue Oil Field north of U.S. Highway 101 near El Rio. There are also several smaller abandoned oil fields. Oil facilities are interspersed with agricultural land uses both east and west of Oxnard.[9]  HistoryPrehistory and indigenous peoplesHuman settlement at over 5000 B.C.E. has been documented in nearby coastal sites. These prehistoric sites may contain middens, milling stone sites, large villages, cemeteries, and tool making sites. The diversity of natural resources along with the temperate climate with a long growing season produced a lengthy archaeological record of human activity along the coast. Calleguas Creek and the Santa Clara River were populated with many Native American villages as evidenced by archaeological sites such as the Calleguas Creek Site that was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976.[10] Several sites have also been documented at Mugu Lagoon. The numerous archaeological sites in the adjacent Santa Monica Mountains also demonstrate the long history of human habitation.[11] Many of the sites are located adjacent to permanent water sources as the presence or absence of water is a crucial predictor of site location in Southern California. Many of the archaeological sites on the plain have been disturbed by erosion, farming, gophers, bulldozers, and other cultural and natural sources of disturbance.[12] Spanish period (1782 to 1822)Spanish explorers made sailing expeditions along the coast of southern California between the mid-1500s and mid-1700s. In the 18th century, Spain began the colonization and inland exploration of Alta California. They established a tripartite system consisting of missions, presidios, and pueblos. Mission San Buenaventura was founded in 1782 next to the Ventura River, 10 miles (16 km) upcoast from the Santa Clara River. The Oxnard plain was used for grazing herds of livestock which required thousands of acres. The traditional way of life of the Chumash people became increasingly unstable and unsustainable on the Oxnard Plain with the introduction of these animals. They also experienced further disruptive contacts through the increasing number of Europeans and Americans that visited the California coast looking for pelts from fur-bearing animals such as sea otters, and trade in hides and tallow beginning in the 1790s. The destruction wrought by the livestock and shortages of wild plants that they used for food may have made the missions appear to be the only viable alternative to a disintegrating way of life. At its peak in 1816, the mission had over 41,000 animals including 23,400 cattle, 12,144 sheep. The 4,493 horses constituted one of the largest stables of horses of the California mission sites. The Chumash culture, including political and social relationships between communities, trade, and inter-village marriage patterns, could not be sustained as more and more Indians abandoned their traditional way of life and entered the mission. The severe decrease in the Chumash population was in response to a complex set of social, economic, and demographic factors.[13] Mexican period (1822-1848)Mexico gained its independence from Spain in 1821. With the secularization of the missions by the Mexican government in June 1836, their lands were granted as rewards for loyal service or in response to petitions by individuals. Most of the arable land was divided up into large ranchos by 1846.[14] This opened up the Oxnard Plain to further settlement by Europeans.[13] Control of the area was transferred to the United States under the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and California became the 31st state in the Union in 1850. Many Mexican residents and residents who had immigrated from European countries became U.S. citizens. Initial European migrationMany of the Spanish and Mexican rancho families benefited when the cattle market peaked between 1848 and 1855 due to the California Gold Rush.[15] Cattle ranching declined drastically when a drought hit the area in 1863.[16] James Saviers bought property in Rancho Colonia in 1862. He was a blacksmith and farmer who grew and sold eucalyptus trees used to protect crops from the seasonal Santa Ana winds that originated inland and brought strong, hot, extremely dry winds to the treeless plain.[17] Settlers Gottfried Maulhardt and Christian Borchard along with Christian's son, John Edward, and nephew, Caspar began farming with 30 acres (12 ha) of wheat and barley in 1867.[18] New markets for the grain opened up when a shipping wharf was first constructed in 1871 at Hueneme.[19] Irish immigrant Dominick McGrath arrived in 1874 with his wife and children to begin farming on the plain.[20] Johnnas Diedrich, with his bride, Matilda, began a new life of farming in 1882 having come from Hanover, Germany.[21] New Jerusalem was founded in 1875 along the south bank of the Santa Clara River. The community, eventually renamed El Rio, was along the route between Ventura and Hueneme. Lima beans became the dominant crop as they could be grown with very little maintenance.[22] Farmers were actively growing trial fields of sugar beets in 1897.[23]  City development and growthIn 1887, as the railroad was constructed from Los Angeles to the town of San Buenaventura, the Montalvo station was established on the plain on the north side of the river. In 1898 the Montalvo Cutoff brought the railroad across the Santa Clara River at El Rio and then due south to where the town of Oxnard was being established. The Oxnard Brothers built the American Beet Sugar Company factory on land in the middle portion of the plain that they bought from James Saviers.[17][24] He became a judge and an honorary justice of the peace: Saviers Road was named after him in the new city of Oxnard that arose around the factory.[17] The railroad continued with tracks heading east out of Oxnard and eventually being extended to Santa Susana in Simi Valley. Traffic on the coast railroad line was rerouted through Oxnard in 1904 with the completion of the Santa Susana Tunnel as this became the most direct route between Los Angeles and San Francisco.[25] Agriculture as an industry, as differentiated from family farming, began with the access to the railroad network. In 1903, this transition in agriculture labor practices found Japanese and Mexican sugar beet workers and labor contractors united in protest as the growers, backed by financiers, slashed the wage rate by 50 percent and sought to eliminate independent labor agents. The workers formed the Japanese Mexican Labor Association to press their concerns. While one ethnic group can often be pitted against another to undermine labor solidarity, the Oxnard Strike of 1903 unified them, as their efforts brought the industry to a standstill until their demands were met.[26] In 1911, J. Smeaton Chase noted the "prosperous fields of beans and beets" as he descended from the Santa Monica Mountains onto the Oxnard Plain during his 2,000-mile (3,200 km) horseback journey from Mexico to Oregon. In his book about the journey, he describes the "sleepy little coast village of Hueneme" as a "ghost of a once flourishing town" due to the establishment of a beet sugar factory. The once busy port had drastically declined as passenger and freight traffic shifted to the railroad.[27] Postwar and modern development Although agriculture has long been important to the economy on the Oxnard Plain, the booming growth in the 1960s of the cities located on the plain expanding by building housing, highways, and associated infrastructure over the rich agricultural land.[28][29] Several methods were tried to encourage the building in compact, connected ways and reduce urban sprawl into the agricultural lands. "Guidelines for orderly development" were adopted in 1969 by the County of Ventura to encourage urban development to be located within incorporated cities whenever or wherever practical. Eventually greenbelt agreements were established between cities to further define the areas of growth.[30] A growth control ordinance was adopted by the city of Ventura in 1995.[31] "Save Open-space and Agricultural Resources" (SOAR) was the name given to these plans that would limit housing and commercial development on farmland surrounding the cities.[32] Jean Harris and other activists pressured the Oxnard city council to present a measure to the voters. Oxnard, Camarillo and Ventura County SOAR initiatives were overwhelmingly approved by voters in 1998. Under SOAR, the farmland and open space outside each city's urban growth boundary could not be rezoned without voter approval through 2020.[33][34] The City of Ventura SOAR regulations expire at the end of 2030.[33][35] Ballot initiatives in 2016 proposed to extend the growth control ordinance for another 30 years.[36][37] As measures to renew SOAR were placed on the ballot county-wide in 2016, an alternative proposal was put forth by the agricultural interests.[38] As of 2014[update], farmland values in California were at historic highs and the agricultural industry was optimistic and even confident about the future.[39][40] Pesticide use is an issue in the interface between agriculture and residential areas along with public uses such as schools.[41][42]  While the vast fields of fertile soil were appreciated for the agricultural bounty that could be produced, the sand dunes and wetlands along the coast line were considered useless except as places to dispose of solid and liquid waste. This at least dates back to 1898 when the beet sugar factory sent the wastewater discharge through a pipe to Ormond Beach. Various other areas near the coast were used for dumping trash and oil-waste, much of the time with local government encouragement and supervision.[43] The Halaco Engineering Co., a metal recycling facility at the Ormond Beach wetlands, deposited process wastes and wastewater from the smelter from 1965 until 2004 on what was allegedly a former open dump operated by the City of Oxnard until 1962. The waste pile contains an estimated 112,900 cubic yards (86,300 m3) and the facility has been designated a Superfund site.[44] Other large, polluting industries were cited at Ormond Beach wetlands before environmental concerns highlighted the importance of restoring the area to serve as a dynamic habitat for a wide array of native plants and animals.[45] Over the years, many communities have attempted to control the Santa Clara River by establishing dumps along the banks to create levees that would keep the river from flooding adjacent lands during occasional years with heavy winter rains. Three dump sites about 2 miles (3.2 km) upstream from the mouth of the river came under the control of the Ventura Regional Sanitation District by 1988. They continued to use the sites until they were closed in 1996.[46] Municipal wastewater treatment facilities, industrial dischargers, and power generating stations are point source dischargers along the coast of the Oxnard plain. Water quality at the numerous beaches has been very good with a few exceptions.[47] Two power generating stations were built in the 1960s to take advantage of the ocean for cooling.[48] Reliant Energy purchased the Mandalay Generating Station from Southern California Edison in 1998.[49] The Oxnard City council tried to prevent a third plant from being built in 2012. After years of legal tussles, the 45 megawatts (60,000 hp) McGrath Peaker Plant was built by Edison next to the power plant at Mandalay.[50]
GeographyThis plain is bounded by the Santa Monica Mountains, the Santa Susana Mountains, the Topatopa Mountains to the north, the Santa Clara River Valley to the northeast and the Santa Barbara Channel to the south and west.[6] The topography of the plain is relatively level. It has been formed chiefly by the deposition of sediments from Santa Clara River Valley and the watershed of Calleguas Creek before they flow into the Pacific Ocean.[6] The alluvial deposits from these rivers are generally a few hundred feet (30 metres) thick and lie over Pleistocene and Pliocene sedimentary rocks.[51] The Santa Clara River is one of the largest river systems along the coast of Southern California and only one of two remaining river systems in the region that remain in their natural states and not channelized by concrete.[52] Prior to the agricultural expansion, installation of drainage systems, and other disturbances, this broad, flat, coastal area contained a series of marshes, salt flats, sloughs, and lagoons.[53]: xix Historically, Calleguas Creek flood flows spread across the floodplain and the deposited sediment created the rich agricultural lands of the Oxnard Plain. With year-round agriculture in the floodplain, concrete channels and dirt levees have been built to contain the flow. This has delivered increased sediment to Mugu Lagoon and flooding during extreme rain events.[54]: 4–13 The 16.5-mile-long coastline (26.6 km) is among the longest stretches of continuous, linear beaches in the state. With the Port of Hueneme, Channel Islands Harbor, and Ventura Harbor along with a number of breakwaters, jetties and groins, this is one of the most engineered coastlines in the state with complicated coastal geography.[7]: 56 [55] Groundwater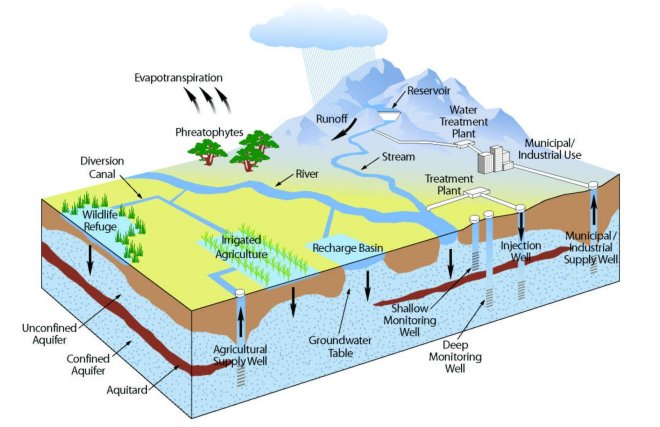 Saltwater intrusion from the ocean has occurred in the southern Oxnard Plain due to the overdraft of groundwater. The Santa Clara Irrigating Company was formed in 1870 and drew water from the Santa Clara River, using a ditch system to irrigate the grain crops.[19] Early settlers began pumping soon afterwards to support farming activities with what at first was a more reliable source. In the modern era, much of the groundwater has been rendered useless for agricultural or potable uses by salt-water intrusion. Unlike coastal Los Angeles and Orange County, Ventura County has no barrier in place to prevent the ocean water from intruding into the inland aquifers.[56] The Sustainable Groundwater Management Act signed into California law in 2014 created a framework for sustainable, local groundwater management for the first time in California history. In response, the Ventura County Board of Supervisors passed an emergency ordinance that halted well-drilling in the Oxnard Plain. Groundwater levels experienced a decrease during the 2012–2013 drought.[57] Calleguas Municipal Water DistrictCalleguas Municipal Water District, a water wholesaler, serves about 75 percent of Ventura County's population. Calleguas ships state water from the Delta to Oxnard, Port Hueneme, and Camarillo on the Oxnard Plain and Moorpark, Thousand Oaks, Simi Valley and unincorporated areas in the east county.[58] These areas also use groundwater and surface water supplies but these sources have increased in salinity. The source of the salts is a combination of agricultural, industrial, and residential activities in conjunction with salts in the imported water.[56] The United Water Conservation District funded a detailed feasibility study in 2014 and found that the impaired groundwater in the south Oxnard Plain is suitable for treatment by reverse osmosis at an acceptable recovery range of 72 to 80 percent.[56] Many local agencies, particularly those in the Calleguas Creek Watershed, have built or are putting in desalters to treat salty groundwater. The treated water can be used for drinking supplies which will make the region less dependent on imported state water. The remaining salt concentrate will be sent out to sea through the Calleguas Regional Salinity Management Project. This $220 million pipeline project started in 2003 and stretches from the marine outfall into Simi Valley.[58][59] That pipeline services desalters in Simi Valley, Moorpark and the Camrosa Water District in the Santa Rosa Valley. Camarillo and Santa Rosa ValleyThe city of Camarillo water system serves about two-thirds of its residents.[60] It imports about 60 percent of its water from the state water project through the Calleguas Municipal Water District and 40 percent is pumped from three wells. The North Pleasant Valley Desalter Project is a $66.3 million project to treat brackish well water.[61][62] The project began construction in September, 2019.[63] The city held a ribbon cutting ceremony in November 2021 as the plant began to operate.[64] After extensive testing and adjustments, the plant started producing water for the city in January 2023.[65] The Camrosa Water District serves nearly 30,000 people in Camarillo and the Santa Rosa Valley along with agricultural customers.[66] The district, which covers 31 square miles (80 km2) is headquartered in Camarillo. Camrosa completed the Round Mountain Water Treatment Plant, a desalting facility, in 2015. It cleans up brackish groundwater and produces 1,000 acre-feet (1,200,000 m3) of drinking water a year. The facility was the first paying customer for the Calleguas Regional Salinity Management Project.[66][67] OxnardIn 2008, the city started up a desalination plant near the Oxnard Transit Center that treats the brackish groundwater from nearby wells.[68] The water supply in the Oxnard Plain has been expanded by a $71 million Advanced Water Purification Facility (AWPF) built by the city of Oxnard. The plant scrubs treated sewage water to super-clean levels that can be used on crops, by industrial customers, and for water landscaping. The water can also be injected into the ground from where it can be pumped out months later for use in the drinking supply.[69] When the final permits were in place, the AWPF began providing water to a lake at the River Ridge Golf Course in 2015. Water from the lake is used to irrigate the golf course. Gradually, pipelines begin serving city parks, street medians, and all the landscaping in new developments including two along the Santa Clara River: RiverPark, a community of 1,800 homes and Wagon Wheel with 1,500 apartments and condos.[70] The water is also provided to industrial customers and farmers near the plant. Initially pipelines needed to reach additional farmers served by the Pleasant Valley County Water District with 15,200-acre-foot a year (18,700,000 m3) were not finished until 2016 but the district was able to temporarily use the brine line to get the water to the farmers during the drought.[71][72][73][74] United Water Conservation DistrictFormed in 1950, the United Water Conservation District battles groundwater overdraft through a combination of aquifer recharge and providing alternative surface water supplies. The District encompasses about 214,000 acres (87,000 ha)[75] and owns Lake Piru and key facilities along the Santa Clara River that are used to manage groundwater supplies.[76] The United Water Conservation District provides wholesale water delivery through three pipelines to various portions of the Oxnard Plain. One is the Oxnard/Hueneme system which serves the City of Oxnard, the Port Hueneme Water Agency (City of Port Hueneme, Channel Islands Beach CSD) and the Naval Base Ventura County (Point Mugu and the Construction Battalion Center).[77] A second pipeline serves agricultural uses in the Oxnard Plain.[78] The third system supplies water to the Pleasant Valley area located between Oxnard and Camarillo.[79] United rates for non-agricultural uses are at least three times more than agricultural users are charged as required by the state water code.[80] The Vern Freeman Diversion Dam, built by United Water in 1991 on the Santa Clara river, channels water to shallow basins designed to replenish the aquifer.[81] For decades before the structure was built, earthen dams were constructed in the river to divert water to farmers and replenished the aquifer. The berms would have to be rebuilt whenever winter rains created a flow that breached the berms.[82] Southern California Steelhead were declared endangered in 1997 and the fish ladder on the structure was deemed insufficient. The National Marine Fisheries Service determined that fixing this was a high priority since it is the first structure the steelhead encounter when attempting to migrate from the ocean.[83] United released water from Lake Piru to specifically recharge the Fox Canyon in the Oxnard Plain for the first time in 2019.[84][85] Ormond Beach Ormond Beach is a 1,500 acres (610 ha) broad, flat, coastal area on the south side of the Oxnard Plain that historically contained marshes, salt flats, sloughs, and lagoons. The expansion of agriculture and industry have drained, filled and degraded much of the wetlands over the past century but the area does have a dune-transition zone–marsh system along much of two-mile-long beach (3.2 km) that extends from Port Hueneme to the northwestern boundary of Point Mugu Naval Air Station.[86][29][87] HazardsThe coastline is subject to inundation by a tsunami up to 23 feet in height.[88] See also
References
Further reading
|
||||||||


