|
Adrenorphin
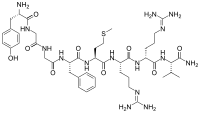
Adrenorphin, also sometimes referred to as metorphamide, is an endogenous, C-terminally amidated, opioid octapeptide (Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met-Arg-Arg-Val-NH2, YGGFMRRV-NH2) that is produced from proteolytic cleavage of proenkephalin A and is widely distributed throughout the mammalian brain.[1][2][3][4][5] It was named based on the fact that it was originally detected in human phaeochromocytoma tumour derived from the adrenal medulla, and was subsequently found in normal human and bovine adrenal medulla as well.[1] Adrenorphin exhibits potent opioid activity, acting as a balanced μ- and κ-opioid receptor agonist while having no effects on δ-opioid receptors.[2] It possesses analgesic and respiratory depressive properties.[6] See alsoReferences
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||