|
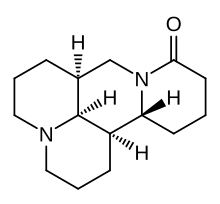
Matrine
Matrine is an alkaloid found in plants from the genus Sophora. It has a variety of pharmacological effects, including in-vitro anti-cancer effects,[1] as well as κ-opioid and μ-opioid receptor agonism.[2][3] Matrine possesses strong antitumor activities in vitro and in vivo. Inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis are the likely mechanisms responsible for matrine's antitumor activities.[4] Matrine is a component of the traditional Chinese medical herb Sophora flavescens Ait. Mu opioid agonism is associated with euphoria, while kappa opioid agonism is associated with dysphoria and psychotomimetic hallucinations (as seen in the kappa-agonist Salvinorin A). Both receptors are known to produce analgesia when activated. Matrine and the related compound oxymatrine have a toxic effect against the formosan subterranean termite.[5] Additionally, it acts as a nematicide against the pine wood nematode which causes pine wilt,[6] as well as pathogenic nematodes which target humans.[7] Matrine alleviates neuro-inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain caused by acute liver injury, thus producing antianxiety and antidepression effects.[8] References
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||